| CPC G01N 21/77 (2013.01) [G01N 31/10 (2013.01); H01L 31/0336 (2013.01); H01L 31/109 (2013.01); G01N 2021/7753 (2013.01); G01N 33/0037 (2013.01); G01N 33/005 (2013.01); G01N 33/0054 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
1. A method of determining an electronic property of a chemical substance without power, the method comprising:
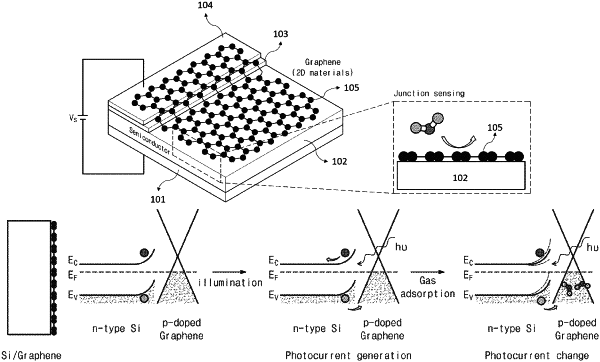
flowing an air comprising the chemical substance to a detecting sensor comprising a bottom electrode, a light absorbing layer comprising n-Si directly disposed on the bottom electrode, an insulating layer directly disposed on a first portion of the light absorbing layer, a top electrode directly disposed on the insulating layer, and a graphene layer directly disposed on a second portion of the light absorbing layer to form a heterojunction therebetween and the graphene layer extending such that it is connected to the top electrode, while irradiating a light to the detecting sensor;
measuring a photocurrent generated by a photoreaction in the heterojunction between the graphene layer and the light absorbing layer comprising n-Si in response to the irradiating of the light absorbing layer in the air comprising the chemical substance without applying a driving voltage to the heterojunction;
measuring a control photocurrent generated from the light absorbing layer in a control air not comprising the chemical substance while irradiating the light to the detecting sensor;
and determining the electronic property of the chemical substance as electron-giving when the photocurrent decreases or as electron-receiving when the photocurrent increases compared to the control photocurrent measured when the control air not comprising the chemical substance flows to the detecting sensor, thereby detecting a presence of the chemical substance according to a change in the photocurrent,
wherein the graphene layer is prepared by a chemical vapor deposition and is not a reduced graphene oxide layer and
wherein the photocurrent generated with 5 ppm of NO2 is at least 1 μA.
|