| CPC F16F 13/106 (2013.01) [F16F 2224/025 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
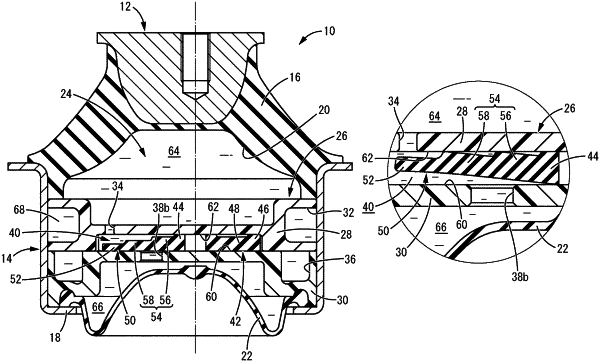
1. A fluid-filled vibration damping device comprising:
a first fluid chamber;
a second fluid chamber;
a partition having a housing area and arranged between the first fluid chamber and the second fluid chamber; and
a movable film having a first surface and a second surface while being housed in the housing area, the movable film comprising:
a central retainer sandwiched and held by the partition;
a plurality of spoke-shaped retainers extending radially outward from the central retainer, the first surface of the movable film being held in a state of being overlapped on a wall inner surface of the housing area of the partition by the central retainer and the spoke-shaped retainers;
an elastic deformation zone provided circumferentially between the spoke-shaped retainers, the elastic deformation zone being allowed to deform in a direction away from the wall inner surface of the housing area on which the movable film is overlapped based on a differential of fluid pressures applied to the first surface and the second surface of the movable film; and
a cushion ridge provided in the elastic deformation zone, the cushion ridge projecting from the second surface of the movable film while extending radially outward from the central retainer, wherein
a projection height of the cushion ridge is varied in a direction of extension of the cushion ridge such that a timing of contact with an opposing wall inner surface in the housing area varies depending on an amount of deformation of the elastic deformation zone.
|