| CPC E02F 9/2045 (2013.01) [E02F 9/205 (2013.01); E02F 9/261 (2013.01); E02F 9/264 (2013.01); G05D 1/0214 (2013.01); G05D 1/024 (2013.01); G05D 1/0242 (2013.01); G05D 1/0246 (2013.01); G05D 1/0274 (2013.01); G05D 1/0278 (2013.01); G05D 2201/0202 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
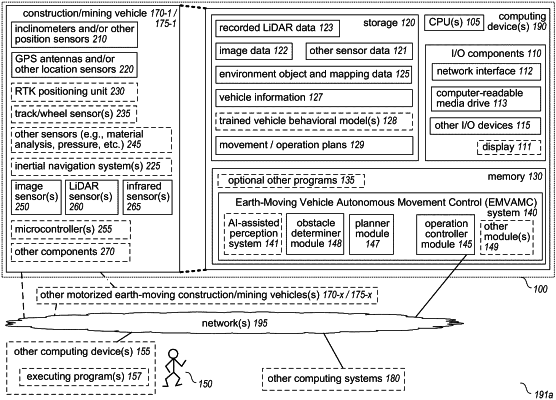
obtaining, from a plurality of sensors mounted on a powered earth-moving vehicle on a job site, vehicle data about the powered earth-moving vehicle, including a track heading direction of one or more tracks of the powered earth-moving vehicle using at least one track sensor, and GPS coordinates for one or more portions of a chassis of the powered earth-moving vehicle using one or more GPS antenna sensors;
obtaining, from a plurality of additional sensors, environment data about an area of the job site, including at least one of LiDAR data about the area from one or more LiDAR sensors, or visual data about the area from one or more image sensors, and further including infrared data for the area from one or more infrared sensors mounted on the powered earth-moving vehicle;
classifying, by one or more configured hardware processors and based at least in part on the environment data, an obstacle located on a path between a current position of the powered earth-moving vehicle on the job site and a target destination location on the job site, wherein the classifying of the obstacle is based in part on the infrared data and includes using one or more trained machine learning models to determine whether the obstacle is at least one of a person or an animal;
monitoring, by the one or more configured hardware processors, and after the classifying and using one or more of the additional sensors, the obstacle to detect whether the obstacle is moving;
determining, by the one or more configured hardware processors, and based at least in part on the classifying and on the monitoring of the obstacle to detect whether the obstacle is moving, information about the obstacle that includes the obstacle is the at least one of the person or the animal based at least in part on the infrared data for the obstacle being above a defined temperature threshold;
determining, by the one or more configured hardware processors and based at least in part on a combination of the vehicle data and the environment data, to perform autonomous operations of the powered earth-moving vehicle that include inhibiting movement of the powered earth-moving vehicle until the obstacle is no longer located on the path in response to the obstacle being determined to be the at least one of the person or the animal; and
initiating, by the one or more configured hardware processors, the determined autonomous operations of the powered earth-moving vehicle.
|