| CPC C10G 55/06 (2013.01) [B01J 29/088 (2013.01); B01J 29/405 (2013.01); B01J 35/08 (2013.01); B01J 38/02 (2013.01); C01B 3/40 (2013.01); C01B 3/48 (2013.01); C01B 3/56 (2013.01); C01B 2203/0283 (2013.01); C01B 2203/042 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1241 (2013.01); C10G 2300/107 (2013.01); C10G 2300/1077 (2013.01); C10G 2300/202 (2013.01); C10G 2300/205 (2013.01); C10G 2300/4018 (2013.01); C10G 2400/20 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
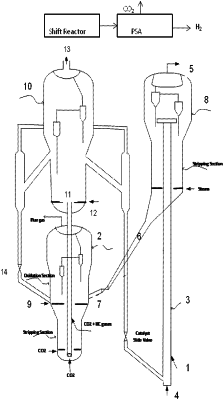
1. A process for conversion of a residue hydrocarbon feedstock having a feed CCR of more than 5 wt % into hydrogen and light olefins, the process consisting of:
(a) cracking the residue hydrocarbon feedstock along with steam in a riser reactor in presence of a multifunctional micro spherical catalyst from a reformer to obtain a reaction mixture comprising cracked hydrocarbons, hydrocarbon gases, hydrogen, and a coked catalyst;
(b) separating the coked catalyst and the cracked hydrocarbons obtained from step (a) at an end of the riser reactor and transferring the coked catalyst to a regenerator;
(c) sending the cracked hydrocarbons obtained after separation in step (b) to a main fractionator for fractionation;
(d) regenerating the coked catalyst of step (b) in an upper part of the regenerator by burning carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, metals, and nitrogen deposits on the coked catalyst in presence of oxygen containing gases to obtain a regenerated catalyst;
(e) removing entrapped flue gas from the regenerated catalyst of step (d) at the lower part of the regenerator using CO2 as a stripping medium to obtain a stripped catalyst;
(f) transferring the stripped catalyst of step (e) to a reformer via a transporting pipe or a lift line using CO2 as a lifting medium;
(g) dry reforming the hydrocarbon gases to synthesis gas in the reformer using CO2 and in presence of the stripped catalyst;
(h) recirculating the catalyst from the reformer to the riser reactor and to the upper part of the regenerator; and
(i) sending the synthesis gas from step (g) to a shift reactor for converting carbon monoxide in the synthesis gas to carbon dioxide and hydrogen through water gas shift reaction; wherein the carbon dioxide, hydrogen and unconverted hydrocarbons are sent to a Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) unit for hydrogen separation and off-gas from the PSA unit is recycled back to the reformer,
wherein the cracked hydrocarbons consist of C2 to C4 olefins in a range of 20-40 wt % and total hydrogen yield is in a range of 2-6 wt % on a fresh hydrocarbon feedstock basis.
|