| CPC C03C 17/256 (2013.01) [C03C 23/0025 (2013.01); C03C 23/0075 (2013.01); B82Y 40/00 (2013.01); C03C 2217/212 (2013.01); C03C 2218/11 (2013.01); C03C 2218/32 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
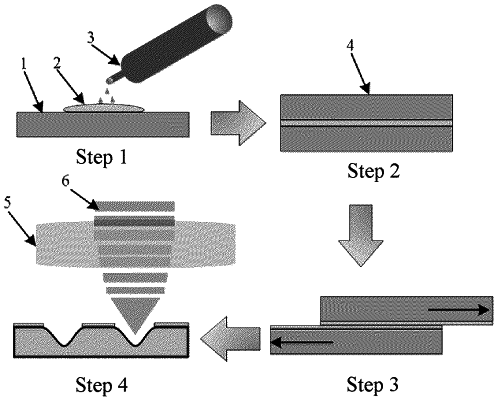
1. A method for preparing a microstructure on a surface of glass by titanium oxide nanoparticle-assisted infrared nanosecond laser, comprising:
dropwise applying a titanium oxide nanoparticle hydrogel onto the surface of a glass sample;
then pressing another piece of glass on the surface of the titanium oxide nanoparticle hydrogel, so that the titanium oxide nanoparticle hydrogel is evenly distributed between the two pieces of glass, and allowing the two pieces of glass to stand horizontally until the titanium oxide nanoparticle hydrogel is solidified;
separating the two pieces of glass to obtain a glass with a uniform titanium oxide nanoparticle coating;
forming a microstructure using laser; and
performing after-treatment to obtain a glass sample with the microstructure;
wherein a concentration of the titanium oxide nanoparticle hydrogel is 35-40%;
wherein a volume of the titanium oxide nanoparticle hydrogel per unit area is 0.1-0.2 μL/mm2;
wherein the laser is infrared nanosecond laser, a wavelength of the infrared nanosecond laser is 1064 nm, and laser processing parameters comprise an average laser power of 2 W-10 W, a pulse frequency of 20-200 kHz, and a scanning speed of 1000-2000 mm/min; and
wherein the after-treatment includes ultrasonically cleaning the glass sample with acetone, absolute ethanol, and deionized water respectively to remove titanium oxide nanoparticles attached to the surface.
|