| CPC B41J 2/16511 (2013.01) [B41J 2/16523 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
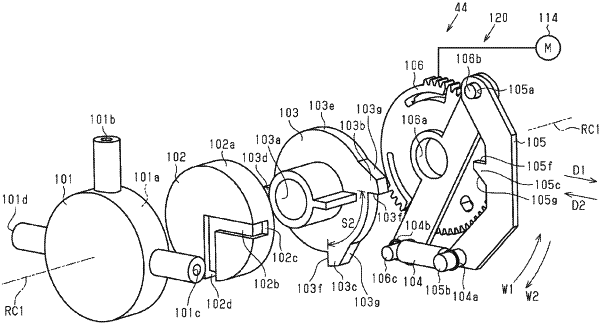
1. A switching mechanism, comprising:
a first rotating body that performs forward rotation and reverse rotation by receiving a driving force transmitted from a driving source; and
a second rotating body that rotates around a center of rotation of the first rotating body and has a plurality of convex portions provided on an outer circumference at intervals in a direction of rotation; wherein
the first rotating body has an engagement portion configured to move along the outer circumference of the second rotating body,
when the first rotating body rotates in a forward direction, engagement of the engagement portion with the convex portion causes rotation of the second rotating body in the forward direction together with the first rotating body,
when the first rotating body rotates in a reverse direction, the engagement portion moves along the outer circumference of the second rotating body so that the second rotating body does not rotate in the reverse direction,
a rotational position of the second rotating body is switched into a predetermined rotational position by causing the first rotating body, driven by the driving source, to execute forward-and-reverse rotational operation, in which forward rotation and reverse rotation are performed sequentially,
a first interval, which is at least one of the intervals, is larger than other intervals,
a central angle formed with respect to the center of rotation by two convex portions forming the first interval is defined as a first angle, and largest one of central angles formed with respect to the center of rotation by respective two convex portions forming the other intervals is defined as a second angle, and
given above definition, the driving source causes the first rotating body to perform forward-and-reverse rotational operation repeatedly by a rotation angle that is smaller than the first angle and is not smaller than the second angle, thereby positioning the engagement portion into the first interval.
|