| CPC A61M 5/142 (2013.01) [A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61B 5/4839 (2013.01); A61B 5/486 (2013.01); A61B 5/4866 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A61M 5/168 (2013.01); A61M 5/172 (2013.01); A61M 5/1723 (2013.01); G16H 10/65 (2018.01); G16H 20/17 (2018.01); G16H 40/60 (2018.01); G16H 40/63 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); A61M 2005/14208 (2013.01); A61M 2205/18 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3576 (2013.01); A61M 2205/502 (2013.01); A61M 2205/507 (2013.01)] | 27 Claims |
|
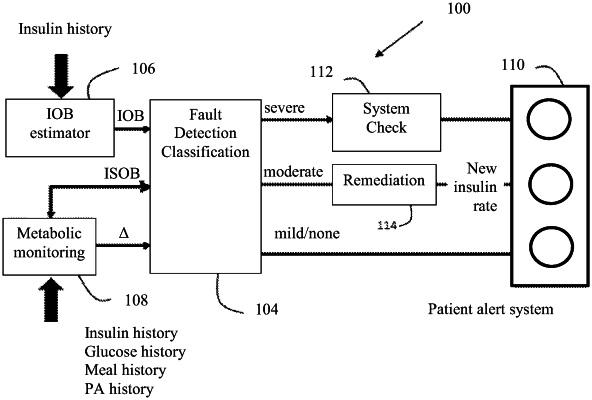
10. A computer-implemented method for monitoring and delivering insulin, comprising:
tracking, by at least one insulin on board estimator processor in real time, insulin on board (IOB) of a patient, IOB being an amount of insulin active and/or an amount of insulin to be active in the patient;
receiving feed-forward signals and calculating, by at least one monitoring processor and Kalman filtering, an amount of insulin need of the patient, wherein the amount of insulin need of the patient is calculated by insulin that should be on board (ISOB)-IOB, wherein the ISOB is based on an estimation or a prediction of patient glucose level;
comparing, by at least one fault detection and classification processor, the amount of insulin active in the patient and/or the amount of insulin to be active in the patient with the amount of insulin need of the patient;
determining, by the at least one fault detection and classification processor, an insulin fault level based on the comparison; and
automatically changing, via a remediation module and in response to determining the fault level, insulin delivery by an insulin delivery device such that the amount of insulin active in the patient approaches the amount of insulin need of the patient.
|