| CPC A61B 8/5207 (2013.01) [A61B 8/5292 (2013.01); A61B 8/54 (2013.01); A61B 8/585 (2013.01); G06N 3/04 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
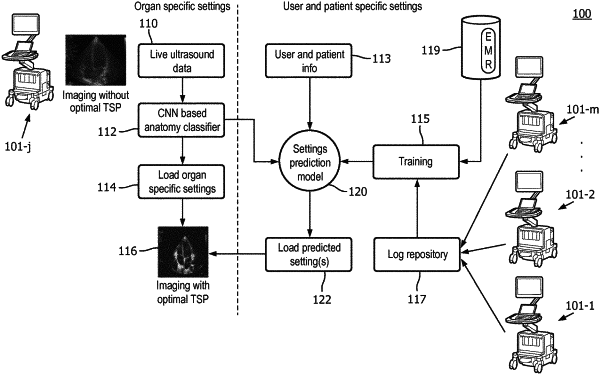
1. An ultrasound imaging system with automated setting of imaging parameters during live imaging, the system comprising:
a probe configured to transmit ultrasound toward a subject for generating ultrasound images of biological tissue of the subject;
a processor configured to generate and to cause the ultrasound imaging system to display, in real-time, a live stream of ultrasound images of the biological tissue in accordance with a plurality of imaging parameters of the ultrasound system, wherein the processor is further configured to:
receive, in real-time, an ultrasound image from the live stream of ultrasound images;
receive an identification of a type of the biological tissue in the ultrasound image;
receive subject identification information, user identification information, or a combination thereof;
identify the subject as a recurring subject based at least in part on the subject identification information;
based on the type of the biological tissue and the subject identification information, generate at least one predicted setting for the recurring subject for at least one of the plurality of imaging parameters; and
apply the at least one predicted setting to the respective imaging parameter for subsequent live imaging of the recurring subject,
wherein the processor is configured to generate the at least one predicted setting using an artificial neural network model, and
wherein the artificial neural network model is a model trained using historical data extracted from system logs from multiple prior scans performed by a same user or of the recurring subject.
|