| CPC A61B 8/12 (2013.01) [A61B 8/445 (2013.01); A61B 8/4472 (2013.01); A61B 8/461 (2013.01); A61B 8/54 (2013.01); A61B 8/565 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
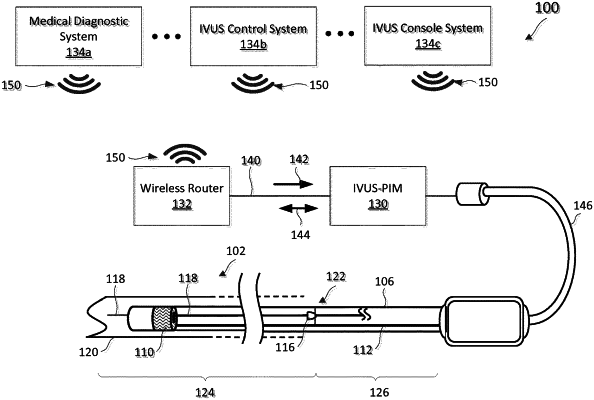
1. An intraluminal imaging system, comprising:
an intraluminal device comprising an ultrasound imaging component configured to be powered to obtain an ultrasound echo signal while the intraluminal device is positioned within a body lumen of a patient;
a wireless router;
a computing device in wireless communication with the wireless router;
a patient interface module (PIM);
a first cable coupled to the wireless router and the PIM, wherein the first cable comprises a network cable; and
a second cable coupled to the PIM and the intraluminal device,
wherein the PIM comprises:
a single housing such that only the first cable, the single housing, and the second cable are communicatively positioned between the wireless router and the intraluminal device;
a power-over-network component disposed within the single housing and different than the network cable, wherein the power-over-network component is configured to:
receive operating power from the wireless router at the PIM via the network cable;
provide at least a portion of the operating power from the PIM to the intraluminal device via the second cable such that the ultrasound imaging component is powered to obtain the ultrasound echo signal; and
at least one of a field programmable gate array (FPGA) or a processor disposed within the single housing and configured to:
receive the ultrasound echo signal; and
determine ultrasound image data based on at least the ultrasound echo signal,
wherein the power-over-network component is further configured to:
transmit the ultrasound image data to the computing device via the network cable and the wireless router such that data communication for the ultrasound image data is provided via the network cable.
|