| CPC A61B 6/025 (2013.01) [A61B 6/027 (2013.01); A61B 6/4085 (2013.01); A61B 6/50 (2013.01); A61B 6/5205 (2013.01); A61B 6/5217 (2013.01); A61B 6/5247 (2013.01); A61B 6/5258 (2013.01); A61B 6/541 (2013.01); A61B 6/544 (2013.01); A61B 6/547 (2013.01); A61N 5/1067 (2013.01); A61N 5/1068 (2013.01); G01S 17/894 (2020.01); G06T 5/004 (2013.01); G06T 7/11 (2017.01); G06T 7/187 (2017.01); G06T 7/337 (2017.01); G06T 15/06 (2013.01); A61N 2005/1059 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20192 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30064 (2013.01)] | 28 Claims |
|
1. A method of x-ray imaging, comprising:
positioning a patient at a first orientation relative to an x-ray imaging source;
using a 3D imaging technique, distinct from x-ray imaging, to measure one or more positions of the patient's chest;
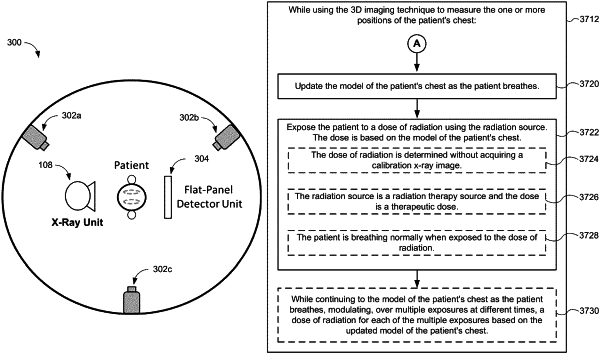
while using the 3D imaging technique to measure the one or more positions of the patient's chest:
generating a model of the patient's chest using the one or more positions of the patient's chest;
updating the model of the patient's chest as the patient breathes; and
obtaining an x-ray image of the patient's chest, including exposing the patient to a dose of radiation using the x-ray imaging source that is calculated using the model of the patient's chest.
|