| CPC A61B 5/026 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02125 (2013.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 11/003 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30048 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30104 (2013.01); G06T 2211/404 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
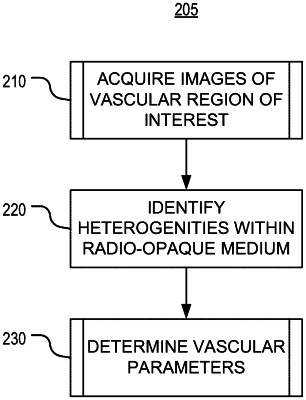
1. A method of determining dynamic vascular parameters of blood flow, comprising:
acquiring two-dimensional projection images of a vascular region of interest at a predetermined frequency, the vascular region of interest being downstream of a site of vascular administration of a radio-opaque medium;
identifying, within the acquired two-dimensional projection images, heterogeneities of the radio-opaque medium, the heterogeneities being generated by the vascular administration of the radio-opaque medium that is temporally discontinuous with high frequency provided by a rotary peristaltic pump; and
tracking, by processing circuitry, a change in position of the heterogeneities within the vascular region of interest, based on the position where a region of particles of the radio-opaque medium is present in the two-dimensional projection images in which the heterogeneities are identified, and determining the dynamic vascular parameters of the blood flow based on the change in position of the tracked heterogeneities of the radio-opaque medium.
|