| CPC H04W 74/0808 (2013.01) [H04W 8/24 (2013.01); H04W 56/001 (2013.01); H04W 72/046 (2013.01); H04W 74/0891 (2013.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
1. A method for wireless communication at a user equipment, comprising:
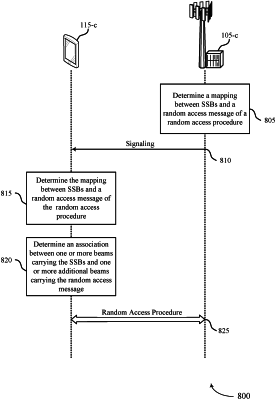
receiving, from a network entity, a configuration of physical random access channel (PRACH) occasions for a two-step random access procedure, the configuration indicating a quantity of synchronization signal blocks associated with a single PRACH occasion of the PRACH occasions and a quantity of contention-based preambles for each of the synchronization signal blocks per valid PRACH occasion of the PRACH occasions;
determining an association between the synchronization signal blocks and a set of PRACH occasions based at least in part on the configuration and an association pattern period of the two-step random access procedure, wherein the association pattern period is based at least in part on a finite range/time domain configured by the network entity;
mapping resources of the synchronization signal blocks to the set of PRACH occasions and one or more physical uplink shared channel resource units over PRACH configuration periods of the association pattern period of the two-step random access procedure based at least in part on the association; and
performing the two-step random access procedure with the network entity based at least in part on the mapping.
|