| CPC H04B 17/3913 (2015.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); H04B 7/0626 (2013.01); H04B 7/0652 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
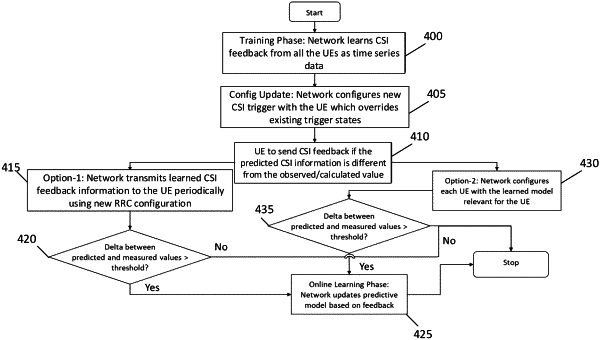
learning channel state information feedback from one or more user
equipment as time series data, wherein the time series data comprises data transmitted by the one or more user equipment which is associated with corresponding time information;
building a predictive model for user equipment feedback based on the learned channel state information feedback;
configuring a channel state information trigger with the one or more user equipment based on the predictive model, wherein the channel state information trigger configures the one or more user equipment to send channel state information feedback when a difference between predicted channel state information and an observed or computed value satisfies a learned threshold value that is learned depending on previous instances of radio link failures and an increase in packet loss rate, wherein channel state information includes CRI-RI-CQI and L1-RSRP values;
transmitting learned channel state information feedback information to the one or more user equipment periodically using a new radio resource control configuration including CSI-PredictInfo;
signaling the predicted channel state information to the one or more user equipment,
generating a learned model from the learned channel state information feedback, wherein the learned model includes time series data using LSTMs and polynomial regression, wherein signaling the predicted channel state information comprises configuring the one or more user equipment with the learned model; and
determining a difference between the predicted and actual channel state information; and
signaling to the one or more user equipment the difference between the predicted and actual channel state information.
|