| CPC G16H 50/30 (2018.01) [G06F 17/18 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
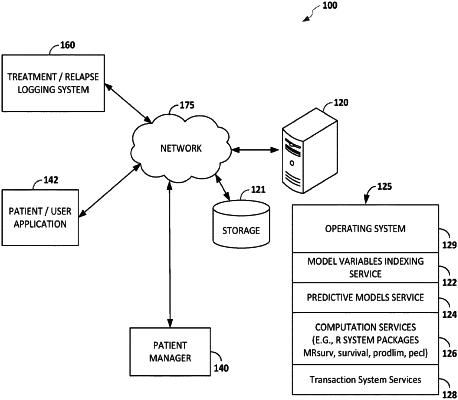
|
1. A method for predicting relapse or non-adherence in an individual subject based on a predictive model, the method comprising:
selecting a cohort of historical subjects in an electronic health records system with known relapse statuses;
retrieving for the selected cohort of historical subjects historical values for variables including one or more of treatment events, medication history, substance use history, demographic attributes, and laboratory tests;
standardizing the retrieved historical values using one or more processors to symmetrize and deskew distributions of ratio-scale or interval-scale variables included inthe retrieved historical values;
performing dimensionality reduction using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression;
based on the LASSO regression, determining a set of statistically-significant independent variables and a set of dependent variables from the symmetrized and deskewed distributions of ratio-scale or interval-scale variables;
performing relative survival regression using multiplicative Cox Proportional Hazards relative survival regression of the set of dependent variables on the set of statistically-significant independent variables;
storing the independent variables' regression coefficients determined by the relative survival regression thereby forming the predictive model for determining likelihood of addiction relapse or non-adherence;
accessing the predictive model and corresponding model variables;
accessing a health record information corresponding to the individual subject, and extracting subject values corresponding to the model variables from the health record information of the individual subject;
standardizing the subject values using one or more processors to symmetrize and deskew ratio-scale or interval-scale values included in the subject values to generate a plurality of standardized values;
utilizing the predictive model and the plurality of standardized values to determinea predicted likelihood of relapse for the individual subject;
comparing the predicted likelihood of relapse with a predetermined threshold; and
responsive to the predicted likelihood of relapse exceeding the predetermined threshold, automatically modifying a care plan for the individual subject and providing the determined likelihood of relapse prediction to a caregiver associated with the individual subject via a notification, wherein modifying the care plan comprises increasing monitoring, modifying a pharmaceutical combination administered to the individual subject, or scheduling a caregiver visit with the individual subject.
|