| CPC G10L 15/197 (2013.01) [G10L 15/063 (2013.01); G10L 15/1815 (2013.01); G10L 15/22 (2013.01); G10L 15/30 (2013.01); G10L 2015/081 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
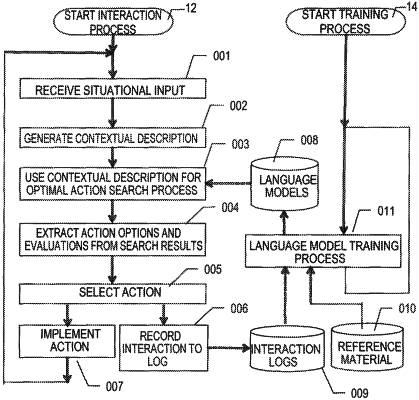
1. An Artificial Intelligence (AI) language virtual agent having self-improvement features which incorporate language modeling and tree search, the virtual agent comprising:
a data processing system having program instructions which are adapted to implement the virtual agent;
the implemented virtual agent accepting as input a current situational description includes natural language input received from an external agent, properties regarding the qualities of the virtual agent, and indicia regarding subject matter context of a present conversation;
wherein the qualities of the virtual agent include temperament and textual tendencies;
wherein the indicia regarding subject matter context includes textual logs from recent conversational exchanges;
wherein the current situational description includes audio, visual and tactile inputs from the external agent which are collected proximate to the virtual agent;
a database of one or more language models, conversation logs storing text from prior textual exchanges, and reference conversations for training;
a combination of self-play engines that train of the language models with self-play and external interaction engines for communicating with external agents; and
a combination of self-moving modules that advance the method of the external agent communicating with the virtual agent via a combination of textual exchanges and one or more audio, visual, and tactile inputs into the virtual agent; and
wherein the virtual agent utilizing tree search techniques in combination with the one or more language models for outputting optimized responses to the current situation description, and wherein the virtual agent responds with self-optimized textual expression to verbal input in combination with the audio, visual, tactile, and other sensory inputs.
|