| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); G06T 7/62 (2017.01); G06T 2207/10048 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10101 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10104 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10108 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10116 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10132 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30101 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method of assessing a state of cardiovascular disease of a subject based on one or more normalized plaque parameters derived from non-invasive medical image analysis, the computer-implemented method comprising:
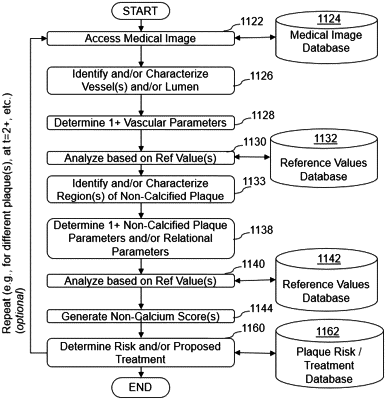
accessing, by a computer system, a medical image of a subject, wherein the medical image of the subject is obtained non-invasively;
analyzing, by the computer system, the medical image of the subject to identify one or more arteries;
determining, by the computer system, one or more vessel parameters associated with the identified one or more arteries, the one or more vessel parameters comprising vessel wall, volume, and curvature of the identified one or more arteries;
analyzing, by the computer system, the medical image of the subject to identify one or more regions of plaque within the identified one or more arteries;
determining, by the computer system, one or more plaque parameters associated with the identified one or more regions of plaque, the one or more plaque parameters comprising plaque volume, location, and geometry of the identified one or more regions of plaque;
determining, by the computer system, a hypothetical vessel volume of the identified one or more arteries without the identified one or more regions of plaque, wherein the hypothetical vessel volume is determined by:
identifying a posterior boundary and an anterior boundary of the identified one or more regions of plaque along the vessel wall of the identified one or more arteries based at least in part on the location and geometry of the identified one or more regions of plaque;
graphically removing the identified one or more regions of plaque from the identified one or more arteries;
interpolating a hypothetical curvature of the identified one or more arteries without the identified one or more regions of plaque based at least in part on the curvature of the identified one or more arteries and the identified posterior boundary and the identified anterior boundary of the identified one or more regions of plaque along the vessel wall of the identified one or more arteries after graphically removing the identified one or more regions of plaque; and
determining the hypothetical vessel volume based at least in part on the volume of the identified one or more arteries and the interpolated hypothetical curvature of the identified one or more arteries without the identified one or more regions of plaque;
normalizing, by the computer system, percent atheroma volume (PAV) by generating a hypothetical PAV value based at least in part on the volume of the identified one or more regions of plaque and the hypothetical vessel volume;
analyzing, by the computer system, the hypothetical PAV value by comparison to a dataset of reference hypothetical PAV values derived from a plurality of medical images of a population with varying states of cardiovascular disease; and
determining, by the computer system, an assessment of a state of cardiovascular disease of the subject based at least in part on analysis of the hypothetical PAV value,
wherein the computer system comprises a computer processor and an electronic storage medium.
|