| CPC G01S 7/4816 (2013.01) [G01S 7/4813 (2013.01); G01S 7/499 (2013.01); G01S 17/02 (2013.01)] | 26 Claims |
|
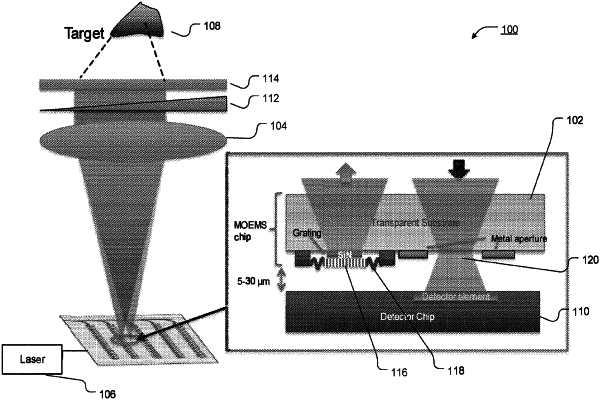
1. A method for operation of a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system, comprising:
producing and projecting a two-dimensional array of light spots on a scene, by an arrayed micro-optic having an array of optical emission sites, using light emitted from a light source, such that the light travels a light path from the arrayed micro-optic to a lens, from the lens to a birefringent prism, from the birefringent prism to a quarter wave plate, and from the quarter wave plate to the scene, wherein the light as reflected from the scene travels from the scene to the quarter wave plate, from the quarter wave plate to the birefringent prism, from the birefringent prism to the lens, and from the lens to receiver optics having an array of optical detection sites; and
receiving, by the receiver optics, the light as reflected from the scene, each of the light spots in the two-dimensional array having a one-to-one correspondence with an optical detection site in the receiver optics, a mask having an array of apertures being located in the light path between the lens and the receiver optics, each of the apertures being located in front of a respective one of the optical detection sites.
|