| CPC G01S 19/246 (2013.01) [G01S 19/24 (2013.01); G01S 19/43 (2013.01); G01S 19/23 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
5. A data processing system adapted for carrier phase ready coherent acquisition of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) snapshot signal, the system comprising:
a host computing platform comprising one or more computers, each with memory and one or processing units including one or more processing cores; and,
an acquisition module comprising computer program instructions enabled while executing in the memory of at least one of the processing units of the host computing platform to perform:
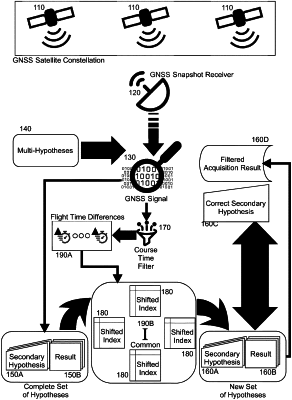
receiving in a snapshot receiver different GNSS signals from correspondingly different GNSS satellites;
performing multi-hypothesis (MH) acquisition upon each of the different GNSS signals in order to produce a complete set of secondary code index hypotheses and corresponding acquisition results by comparing each of the secondary code index hypotheses to each one of the different GNSS signals with a resulting signal having an identified peak at a correct code-phase and Doppler frequency;
adjusting the secondary code index hypotheses for each of the different GNSS signals of the correspondingly different GNSS satellites based upon a flight time difference determined for each of the different GNSS satellites by shifting the secondary code index hypotheses by an integer amount of one of the flight time differences for the respectively corresponding one of the GNSS satellites, the adjustment producing a new set of secondary code index hypotheses for a set of shifted indexes, one for each of the GNSS signals;
filtering the new set to include only ones of the secondary code index hypothesis in the new set having a predominate common index at a common moment in time comprising only those of the shifted indexes of the set of shifted indexes associated with a common index favored by a dominant portion of the shifted indexes; and,
applying remaining ones of the secondary code index hypotheses in the new set to respective ones of the GNSS signals in order to acquire the GNSS signals.
|