| CPC G01S 15/89 (2013.01) [G06T 7/50 (2017.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01)] | 25 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
at a device including one or more processors and non-transitory memory:
obtaining image data including one or more images of a real-world environment;
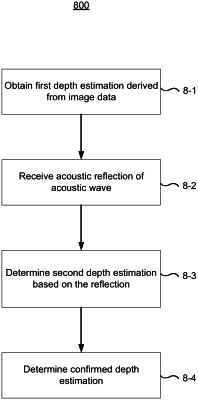
obtaining a first depth estimation characterizing a distance between the device and the real-world environment in a direction relative to the device, wherein the first depth estimation is derived from the image data;
obtaining acoustic data representing audio in the real-world environment;
obtaining a second depth estimation characterizing the distance between the device and the real-world environment in the direction relative to the device, wherein the second depth estimation is derived from the acoustic data, wherein the first depth estimation characterizes a distance between the device and a first surface in the real-world environment and the second depth estimation characterizes a distance between the device and a second surface in the real-world environment different than the first surface; and
in response to determining that a difference between the first depth estimation and the second depth estimation exceeds a threshold value, determining a confirmed depth estimation characterizing the distance between the device and the real-world environment in the direction relative to the device as the second depth estimation.
|