| CPC F16D 48/06 (2013.01) [F16H 48/34 (2013.01); F16D 2500/10425 (2013.01); F16D 2500/3115 (2013.01); F16D 2500/3117 (2013.01); F16D 2500/70647 (2013.01); F16D 2500/70668 (2013.01); F16H 2048/204 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
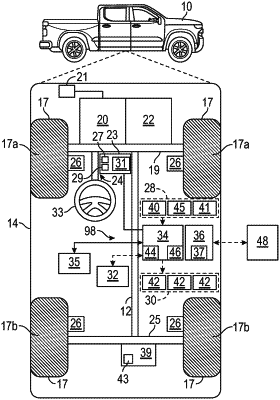
1. A method for determining, in real-time, an electronic limited-slip differential (eLSD) clutch torque, comprising:
receiving vehicle data in real-time, wherein the vehicle data includes a torque request;
determining a preliminary eLSD clutch torque using a neural network and the vehicle data;
determining clutch torque bounds of the eLSD using a physics-based model;
determining whether the preliminary eLSD clutch torque is outside the clutch torque bounds of the eLSD;
in response to determining that the preliminary eLSD clutch torque is outside the clutch torque bounds of the eLSD, adjusting the preliminary eLSD clutch torque using the clutch torque bounds to determine a final clutch torque of the eLSD; and
commanding, in real-time, the eLSD to apply the final clutch torque to a clutch of the eLSD.
|