| CPC C12Q 1/6869 (2013.01) [B82Y 15/00 (2013.01); G01N 27/44743 (2013.01); G01N 33/48721 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
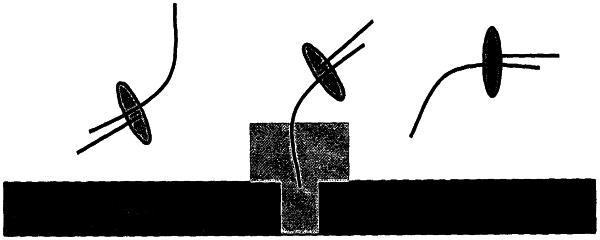
1. A method for detecting analytes, comprising:
(a) providing a membrane in which is present a nanopore that provides a channel through the membrane;
(b) contacting the membrane, in an ionic solution, with one or more analytes, wherein following contact with the membrane the analytes are tethered to the membrane via a tethering group;
(c) applying a potential difference across the membrane and detecting a first analyte using the nanopore, from among the analytes tethered to the membrane; and
(d) detecting a second analyte, from among the analytes tethered to the membrane, using the same nanopore, wherein the second analyte is not the first analyte;
wherein the one or more analytes is an amino acid, peptide, polypeptide, or protein.
|