| CPC A61N 1/36003 (2013.01) [A61N 1/0551 (2013.01); A61N 1/3787 (2013.01); A61N 1/08 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
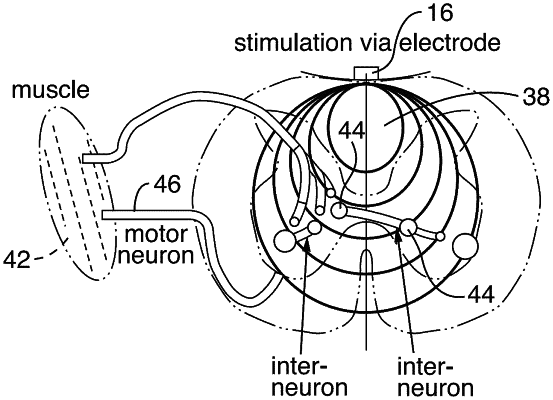
1. A method of performing epidural spinal stimulation for motor function recovery, comprising:
positioning an implantable stimulator circuit having an electrode array configured for coupling to a neural network of a target treatment region of the spine;
generating multi-channel stimulation from the electrode array of said implanted stimulator circuit at the target treatment region;
acquiring bio-impedance data from the electrode array at the target treatment region; and
performing bio-impedance characterization of bio-impedance at the electrode array or an electrode used for sensing, wherein said bio-impedance characteristics are utilized for controlling the stimulation applied at said electrode array according to one or more stimulation parameters that may be adjusted in real time.
|