| CPC A61B 5/073 (2013.01) [A61B 5/05 (2013.01); A61B 5/076 (2013.01); A61B 5/6861 (2013.01); G01B 7/31 (2013.01); G01R 33/022 (2013.01); G01R 33/385 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0223 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for in-vivo monitoring of a target internal volume of a mammal, comprising:
placing the target internal volume proximal to a three-dimensional magnetic field generator;
using the three-dimensional magnetic field generator to sequentially produce:
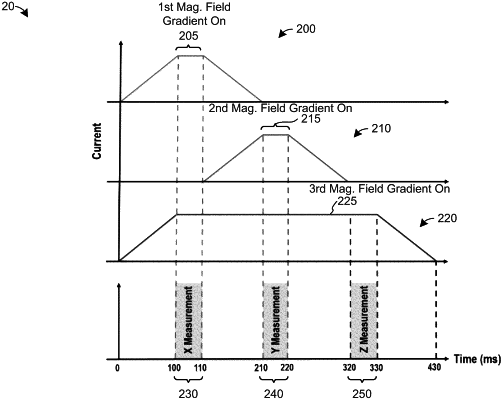
a first localization magnetic field gradient along a first axis, a portion of the magnitude of the first localization magnetic field gradient being monotonically-varying along the first axis through the target internal volume and uniquely encoding a position along said first axis corresponding to a strength of said monotonically-varying first localization magnetic field in said target internal volume, the first localization magnetic field gradient produced at a first time;
a second localization magnetic field gradient along a second axis that is orthogonal to the first axis, a portion of the magnitude of the second localization magnetic field gradient being monotonically-varying along the second axis through the target internal volume and uniquely encoding a position along said second axis corresponding to a strength of said monotonically-varying second localization magnetic field in said target internal volume, the second localization magnetic field gradient produced at a second time that is different than the first time; and
a third localization magnetic field gradient along a third axis that is orthogonal to the first and second axes, a portion of the magnitude of the third localization magnetic field gradient being monotonically-varying along the third axis through the target internal volume and uniquely encoding a position along said third axis corresponding to a strength of said monotonically-varying third localization magnetic field in said target internal volume, the third localization magnetic field gradient produced at a third time that is different than the first and second times;
measuring a total magnetic field magnitude at the first, second, and third times with a three-dimensional magnetic sensor disposed in an ingestible capsule disposed in the target internal volume;
with a controller disposed in the ingestible capsule and in electrical communication with the three-dimensional magnetic sensor, generating a magnetic sensor output signal that encodes a first total magnetic field magnitude measurement, a second total magnetic field magnitude measurement, and a third total magnetic field magnitude measurement that correspond to the first, second, and third magnetic field gradients, respectively;
broadcasting the magnetic sensor output signal from an antenna disposed in the ingestible capsule, the antenna electrically coupled to the controller; and
receiving the magnetic sensor output signal with a receiver;
wherein:
the first localization magnetic field gradient is formed by simultaneously producing:
a first magnetic field with a first planar electromagnet coil set, the first magnetic field having a first-axis magnetic field gradient along the first axis, and
a third magnetic field with a third planar electromagnet coil set, the third magnetic field having a third-axis magnetic field gradient along the third axis, and
the first localization magnetic field gradient comprises a first total magnetic field of the first magnetic field and the third magnetic field.
|