| CPC A61B 5/02427 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02416 (2013.01); A61B 5/7225 (2013.01); A61B 5/725 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0209 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0233 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
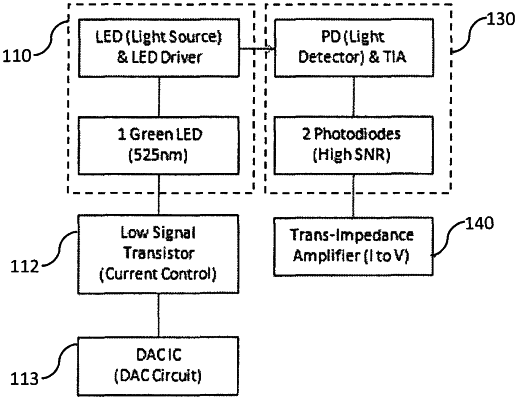
1. A photoplethysmography (PPG) apparatus for determining physiological changes, comprising:
a light source configured to emit a light signal of one wavelength towards a user's skin, the light signal controlled by a driving current to have a variable intensity level dependent on a skin characteristic of the user's skin;
a driving circuit including a signal transistor having a base current for controlling the driving current to alternate the light signal between two ON states and one OFF state, at a frequency of greater than 80 Hz, the two ON states corresponding to two different positive intensity levels of the light signal of the same wavelength for two different skin characteristics;
first and second photodetectors connected in parallel and configured to detect a reflection of the light signal from the user's skin to provide a combined current signal; and
a signal processing circuit operable to convert the combined current signal into a PPG signal for determining the physiological changes.
|
|
16. A photoplethysmography (PPG) method for determining physiological changes, comprising:
emitting, using a light source, a light signal of one wavelength towards a user's skin, the light signal controlled by a driving current to have a variable intensity level dependent on a skin characteristic of the user's skin;
controlling, using a driving circuit including a signal transistor having a base current, the driving current to alternate the light signal between two ON states and one OFF state, at a frequency of greater than 80 Hz, the two ON states corresponding to two different positive intensity levels of the light signal of the same wavelength for two different skin characteristics;
detecting, using first and second photodetectors connected in parallel, a reflection of the light signal from the user's skin to provide a combined current signal; and
converting, using a signal processing circuit, the combined current signal into a PPG signal for determining the physiological changes.
|