| CPC H10N 70/8825 (2023.02) [G11C 13/0004 (2013.01); G11C 13/0069 (2013.01); H10B 63/10 (2023.02); H10B 63/80 (2023.02); H10N 70/066 (2023.02); H10N 70/231 (2023.02); H10N 70/841 (2023.02); G11C 2013/0083 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
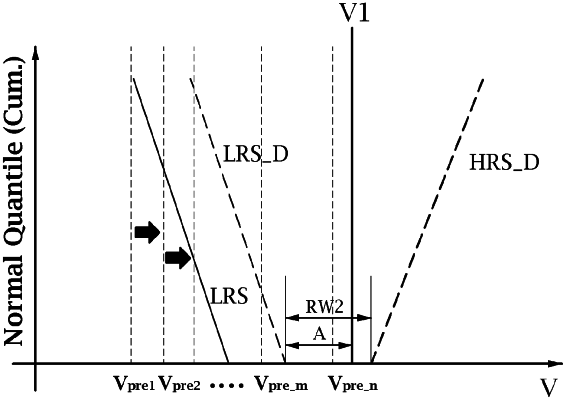
1. A method of initializing a memory cell including a two-terminal selector or a selective memory, which is a chalcogen compound, the method comprising:
(a) applying an initialization voltage to the memory cell;
(b) determining whether the memory cell is turned-on;
(c) when the memory cell is not turned-on;
(i) increasing the initialization voltage;
(ii) determining whether the increased initialization voltage exceeds a first voltage;
(iii) when the increased initialization voltage does not exceed the first voltage, repeating steps (a), (b), and (c) with the increased initialization voltage;
(d) terminating the initializing of the memory cell when either:
(i) the memory cell is determined to be turned-on in step (b), or
(ii) the increased initialization voltage is determined to exceed the first voltage in step (c) (ii);
wherein the initialization voltage applied in the first iteration of step (a) is less than or equal to a maximum threshold voltage of a memory cell in a set state before drift, and
the first voltage is within a drift reading window range, which is the voltage range between a minimum threshold voltage of the memory cell in a reset state expected after the drift and the maximum threshold voltage of the memory cell in the set state expected after the drift.
|