| CPC G01C 21/3461 (2013.01) [B60W 60/0015 (2020.02); B60W 2520/10 (2013.01); B60W 2520/125 (2013.01); B60W 2554/802 (2020.02)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A path planning system for a vehicle comprising:
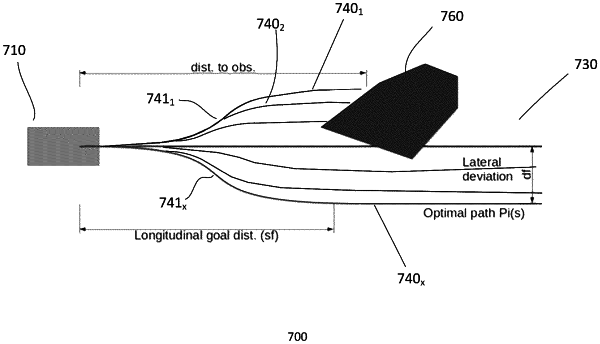
a reactive path planner module, the reactive path planner is based on constrained quintic polynomials, the reactive planner is configured to generate N alternative paths based on a nominal path from location A to location B, the N alternative paths are parallel paths to the nominal path and are displaced within a predefined lateral distance from the nominal path;
a constrainer module, the constrainer constrains the alternative paths based on constrained quintic polynomials, and wherein constraints
ensure safety and comfort of the vehicle based on dynamic and mechanical capabilities of the vehicle, and
comprises
longitudinal distance to an obstacle,
mean curvature,
maximum curvature,
lateral acceleration based on vehicle speed;
time travelling on a path,
lateral distance of a path to the nominal path, or
a combination thereof; and
an evaluator module, the evaluator module applies a cost function to the nominal path and alternative paths and selects one of the paths from the nominal path and alternative paths with a lowest cost from the cost function as an output path of the planning system wherein
longitudinal distance to an obstacle is assigned a highest weight value of the cost function,
mean curvature, time travelling along the path, lateral acceleration and lateral distance to the nominal path constraints are assigned higher weight values of the cost function, and
maximum curvature and lateral distance to previous optimum path are assigned lower weight values of the cost function.
|