| CPC G01C 21/3423 (2013.01) [G01C 21/343 (2013.01); G01C 21/3446 (2013.01); G01C 21/3453 (2013.01); G06Q 10/047 (2013.01); G06Q 50/14 (2013.01)] | 42 Claims |
|
1. A method for electronically computing an itinerary from a departure location to an arrival location for use by a user to plan a trip travelling in a multimodal transportation network, the itinerary being defined as the departure location to an initial station of a multimodal transportation network of predetermined stations, a main part in the multimodal transportation network, a sequence of trips from a set of possible trips within the multimodal transportation network and transfers from a set of feasible transfers within the multimodal transportation network, and a final station of the multimodal transportation network to the arrival location, the method comprising:
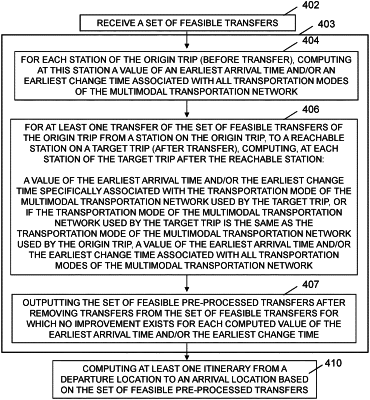
(a) electronically preprocessing the set of feasible transfers to obtain a subset of feasible transfers;
said (a) electronically preprocessing the set of feasible transfers by
(a1) for each station (pti) of the origin trip (t), electronically computing, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, at this station (pti) a value of an earliest arrival time (τA(pti, m)) or an earliest change time (τC (pti, m)) associated with all transportation modes (m) of the multimodal transportation network,
(a2) for at least one transfer (pti→puj) of the set of feasible transfers from a station (pti) on an origin trip (t) to a reachable station (puj) on a target trip (u), electronically computing, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, at each station (puk>j) of the target trip (u) after the reachable station (puj), a value of the earliest arrival time (τA(puk>j, mu) or the earliest change time (τC(puk>j, m)) specifically associated with the transportation mode (mu) of the multimodal transportation network used by the target trip (u), or if the transportation mode (mu) of the multimodal transportation network used by the target trip (u) is the same as the transportation mode (mt) of the multimodal transportation network used by the origin trip (t), a value of the earliest arrival time (τA(puk>j, m)) or the earliest change time (τC(puk>j, m)) associated with all transportation modes (m) of the multimodal transportation network,
(a3) electronically removing, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, before receiving information corresponding to a user's desired mode of transportation, the transfer (pti→puj) from the set of feasible transfers only if determining that each computed value of the earliest arrival time (τA(puk>j, m)) or the earliest change time (τC(puk>j, m)) is not improved by the transfer (pti→puj) and the transfer (pti→puj) is not of a different mode of transportation, thereby preventing a transfer corresponding to a different mode of transportation from being removed from the set of feasible transfers and increasing effectiveness of computing an optimal itinerary consistent with the user's desired mode of transportation, and
(a4) electronically outputting, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, the set of feasible transfers for computing at least one itinerary in the multimodal transportation network, the set of feasible transfers including transfers of all possible modes of transportation;
(b) receiving, after electronically preprocessing the set of feasible transfers, from a user, via a user interface, information corresponding to the user's desired mode of transportation;
(c) electronically determining, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, based upon the set of feasible transfers and the user's desired mode of transportation, a set of possible trips in a multimodal transportation network;
(d) electronically performing, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, a routing optimization algorithm so as to build at least one optimal itinerary, without losing an optimal itinerary corresponding to the user's desired mode of transportation, according to at least one criterion including an earliest arrival time, based upon the set of possible trips in the multimodal transportation network, the routing optimization algorithm electronically computing, using an electronic processor and electronic memory, a Pareto front; and
(e) outputting to the user, via the user interface, the at least one optimal itinerary for use by the user to plan a trip travelling in the multimodal transportation network.
|