| CPC A61B 5/291 (2021.01) [A61B 5/0006 (2013.01); A61B 5/165 (2013.01); A61B 5/168 (2013.01); A61B 5/268 (2021.01); A61B 5/27 (2021.01); A61B 5/305 (2021.01); A61B 5/31 (2021.01); A61B 5/372 (2021.01); A61B 5/4094 (2013.01); A61B 5/6817 (2013.01); A61B 5/7203 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
1. A device for determining a physiological or psychological state of a mammal, the device comprising at least one earpiece comprising:
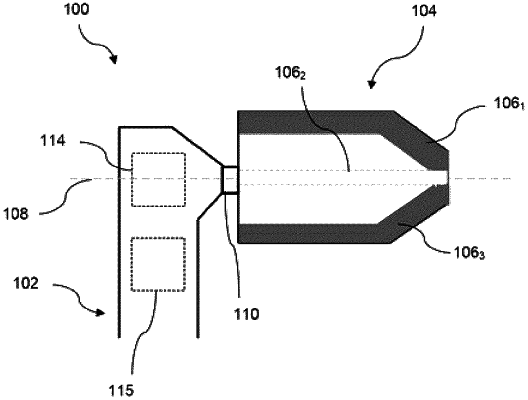
a main body comprising a body of revolution having an axis of revolution;
an endpiece configured to be inserted into a first ear canal, said endpiece having a cylindrical channel intended to receive the body of revolution for detachably mounting the endpiece on the main body, the endpiece being arranged to be movable in rotation about the axis of revolution in order to allow at least one electrode to be oriented toward a zone of a brain of the mammal, and said endpiece comprising a plurality of electrodes arranged on an outer surface of the endpiece, wherein the plurality of electrodes comprises a reference electrode and at least one measuring electrode, each electrode being configured to pick up an electrical signal in the ear canal of the mammal;
first electrical tracks electrically insulated from each other, arranged in the cylindrical channel of the endpiece and connected to the electrodes;
second electrical tracks electrically insulated from each other, arranged in a cylindrical part of the main body and intended to convey the electrical signal, picked up by the electrodes, to a calculation means, wherein each of the first electrical tracks or each of the second electrical tracks has an annular shape having as its axis said axis of revolution and is arranged in electrical contact with one of said first electrical tracks or one of said second electrical tracks, independently of the orientation of the endpiece about said axis of revolution, and said first electrical tracks or second electrical tracks of annular shape being spaced along said axis of revolution;
processing means including two voltage generators which respectively generate a first constant voltage and a second constant voltage; and
calculation means for determining the physiological or psychological state as a function of a potential difference between the electrical signal picked up by the at least one measuring electrode and the electrical signal picked up by the reference electrode, wherein said potential difference fluctuates around a potential corresponding to half a sum of the first and second constant voltages delivered by the two voltage generators.
|