| CPC C07D 405/12 (2013.01) [A61K 45/06 (2013.01); C07D 205/04 (2013.01); C07D 207/08 (2013.01); C07D 213/40 (2013.01); C07D 213/75 (2013.01); C07D 235/14 (2013.01); C07D 263/32 (2013.01); C07D 309/14 (2013.01); C07D 413/14 (2013.01); C07D 487/04 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A compound of Formula (I):
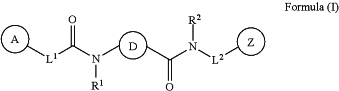 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein:
D is cyclobutyl optionally substituted with 1-4 RX;
L1 is a bond, C1-C6 alkylene, 2-7 membered heteroalkylene, —NRN1—, or —O—, wherein C1-C6 alkylene or 2-7 membered heteroalkylene is optionally substituted with 1-5 RL1;
R1 is hydrogen, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, or C1-C6 alkyl;
L2 is a bond, C1-C6 alkylene, or 2-7 membered heteroalkylene, wherein C1-C6 alkylene or 2-7 membered heteroalkylene is optionally substituted with 1-5 RL2;
R2 is hydrogen, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, or C1-C6 alkyl; or
L2 and R2, together with the nitrogen to which they are attached, form a 4-9 membered monocyclic, bridged bicyclic, fused bicyclic, or spirocyclic heterocyclyl; wherein the 4-9 membered monocyclic, bridged bicyclic, fused bicyclic, or spirocyclic heterocyclyl is optionally substituted on one or more available carbons with 1-5 RW; and wherein if the 4-9 membered monocyclic, bridged bicyclic, fused bicyclic, or spirocyclic heterocyclyl contains a substitutable nitrogen moiety, the substitutable nitrogen may be optionally substituted with RN2;
A and Z are each independently phenyl or 5-6-membered heteroaryl, wherein each phenyl or 5-6-membered heteroaryl is optionally substituted on one or more available carbons with 1-5 RY; and wherein if the 5-6-membered heteroaryl contains a substitutable nitrogen moiety, the substitutable nitrogen may be optionally substituted with RN3; or
one RY, R2, and L2, together with the nitrogen to which R2 and L2 are attached, form a 4-9 membered monocyclic heterocycle, wherein Z is fused to the formed 4-9 membered monocyclic heterocycle, wherein the available carbon atoms of Z are optionally substituted with 1-4 RY; and wherein if Z contains a substitutable nitrogen moiety, the substitutable nitrogen may be optionally substituted with RN3;
each RL1 is independently selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, amino-C1-C6 alkyl, cyano-C1-C6 alkyl, oxo, halo, cyano, —ORA, —NRBRC, —NRBC(O)RD, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)OH, —C(O)ORD, —SRE, —S(O)RD, and —S(O)2RD;
2 geminal RL2 groups together with the carbon to which they are attached form a cyclopropyl moiety; or
each RL2 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, amino-C1-C6 alkyl, cyano-C1-C6 alkyl, oxo, halo, cyano, —ORA, —NRBRC, NRBC(O)RD, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)OH, —C(O)ORD, —SRE, —S(O)RD, and —S(O)2RD;
RN1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C2-C6 alkyl, halo-C2-C6 alkyl, amino-C2-C6 alkyl, cyano-C2-C6 alkyl, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)ORD, and —S(O)2RD;
RN2 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C2-C6 alkyl, halo-C2-C6 alkyl, amino-C2-C6 alkyl, cyano-C2-C6 alkyl, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)ORD, and —S(O)2RD;
RN3 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C2-C6 alkyl, halo-C2-C6 alkyl, amino-C2-C6 alkyl, cyano-C2-C6 alkyl, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)ORD, and —S(O)2RD;
each RW is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, amino-C1-C6 alkyl, cyano-C1-C6 alkyl, oxo, halo, cyano, —ORA, —NRBRC, —NRBC(O)RD, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)OH, —C(O)ORD, —SRE, —S(O)RD, and —S(O)2RD;
each RX is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, amino-C1-C6 alkyl, cyano-C1-C6 alkyl, oxo, halo, cyano, —ORA, —NRBRC, —NRBC(O)RD, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)OH, —C(O)ORD, —SRE, —S(O)RD, and —S(O)2RD;
each RY is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkoxy, amino-C1-C6 alkyl, cyano-C1-C6 alkyl, —O—C1-C6 cycloalkyl, halo, cyano, —ORA, —NRBRC, —NRBC(O)RD, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)OH, —C(O)ORD, —S(RF)m, —S(O)RD, —S(O)2RD, and G1; or
2 RY groups or one RY and one RN3 on adjacent atoms, together with the atoms to which they are attached, form a 3-7 membered fused cycloalkyl, 3-7-membered fused heterocyclyl, fused aryl, or 5-6 membered fused heteroaryl, each of which is optionally substituted with 1-5 RX;
each G1 is independently 3-7-membered cycloalkyl, 3-7-membered heterocyclyl, aryl, or 5-6-membered heteroaryl, wherein each 3-7-membered cycloalkyl, 3-7-membered heterocyclyl, aryl, or 5-6-membered heteroaryl is optionally substituted with 1-3 RZ;
each RZ is independently selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, hydroxy-C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, halo, cyano, —ORA, —NRBRC, —NRBC(O)RD, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, —C(O)OH, —C(O)ORD, and —S(O)2RD;
RA is, at each occurrence, independently hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, halo-C1-C6 alkyl, —C(O)NRBRC, —C(O)RD, or —C(O)ORD;
each of RB and RC is independently hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; or
RB and RC together with the atom to which they are attached form a 3-7-membered heterocyclyl optionally substituted with 1-3 RZ;
each RD is independently C1-C6 alkyl or halo-C1-C6 alkyl;
each RE is independently hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, or halo-C1-C6 alkyl;
each RF is independently hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, or halo; and
m is 1 when RF is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl, 3 when RF is C1-C6 alkyl, or 5 when RF is halo.
|