| CPC A61B 5/443 (2013.01) | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method to identify a subject at risk of developing a food allergy comprising:
a. obtaining a skin sample from the subject, wherein the skin sample is a non-lesional skin sample from the subject;
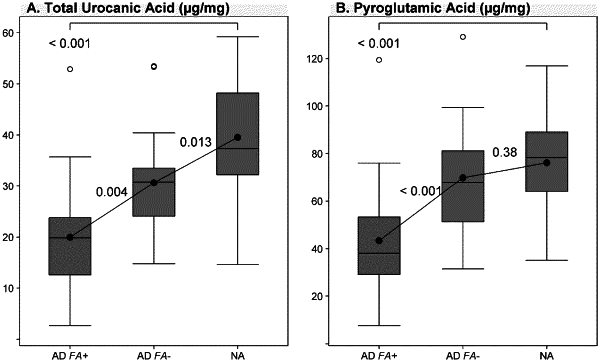
b. determining a level of urocanic acid (UCA), pyroglutamic (PCA) or a combination thereof; wherein the skin sample is obtained by a skin tape stripping method comprising: applying an adhesive tape to a target area of the skin of the subject in a manner sufficient to isolate an epidermal sample adhering to the adhesive tape, wherein the epidermal sample comprises cells from Stratum corneum of the subject, wherein the tape comprises a rubber adhesive; extracting the epidermal sample comprising the UCA, PCA or combination thereof adhering to the adhesive tape with a cell scraper comprising thermoplastic elastomer material in a solvent of about 5% to about 30% alcohol in water; and
c. comparing the level of UCA PCA or a combination thereof in the skin sample to levels of UCA, PCA, or a combination thereof from a control sample wherein a statistically reduced level of UCA, PCA or a combination thereof in the skin sample as compared to the levels in the control sample identifies the subject as being at risk of developing a food allergy, and wherein the control sample is from one or more non-atopic (NA) subjects.
|