| CPC A61B 34/30 (2016.02) [A61B 17/1671 (2013.01); A61B 17/1757 (2013.01); A61B 17/7076 (2013.01); A61B 17/8875 (2013.01); A61B 34/10 (2016.02); A61B 34/32 (2016.02); A61B 34/71 (2016.02); A61B 34/76 (2016.02); A61B 90/98 (2016.02); A61B 17/1615 (2013.01); A61B 17/1626 (2013.01); A61B 17/7032 (2013.01); A61B 17/7082 (2013.01); A61B 17/7092 (2013.01); A61B 2034/105 (2016.02); A61B 2034/107 (2016.02); A61B 34/20 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2051 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2055 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2059 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2068 (2016.02); A61B 90/03 (2016.02); A61B 2090/031 (2016.02); A61B 2090/062 (2016.02); A61B 2090/376 (2016.02)] | 17 Claims |
|
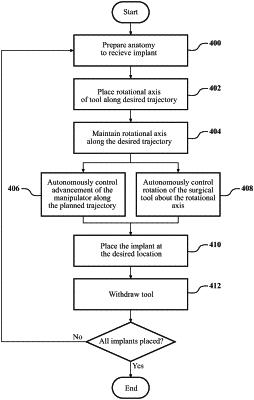
1. A surgical robotic system comprising:
a robotic manipulator;
a surgical tool coupled to the robotic manipulator and configured to hold a screw and to rotate the screw about a rotational axis, the screw having a known thread geometry;
a navigation system configured to track a position of a target anatomy; and
one or more controllers coupled to the robotic manipulator and the navigation system and comprising memory for storing the known thread geometry and wherein the one or more controllers are configured to:
control movement of the robotic manipulator to maintain the rotational axis of the surgical tool along a planned trajectory with respect to the target anatomy based on the tracked position of the target anatomy, and
autonomously control a rotational rate of the surgical tool to rotate the screw about the rotational axis and an advancement rate of the surgical tool to linearly advance the screw along the planned trajectory wherein the rotational rate of the surgical tool and the advancement rate of the surgical tool are proportional to the known thread geometry stored in the memory.
|