| CPC G16B 20/10 (2019.02) [G16B 5/00 (2019.02); G16B 5/20 (2019.02); G16B 20/00 (2019.02); G16B 30/00 (2019.02); G16H 10/40 (2018.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
1. A method for preparing a non-naturally occurring composition of amplified DNA from a test sample useful for determining the likelihood of aneuploidy of a chromosome or chromosome segment of interest in the test sample, comprising:
a. extracting a mixture of fetal cell-free genomic DNA and maternal cell-free genomic DNA from the test sample which is a blood sample of a pregnant woman;
b. preparing a non-naturally occurring composition of amplified DNA extracted in a. by performing amplification of at least 100 polymorphic loci on the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest in a single reaction from the mixture of fetal cell-free genomic DNA and maternal cell-free genomic DNA; and
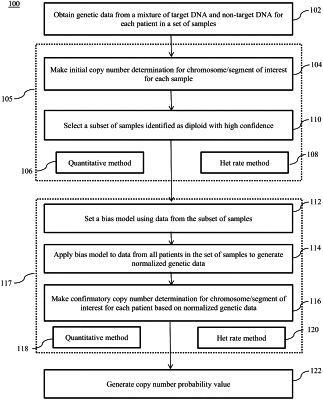
c. analyzing the non-naturally occurring composition of amplified DNA produced in b. by performing sequencing to generate genetic data for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest from each sample in a set of samples comprising the test sample and at least one diploid sample, wherein the genetic data is obtained from a parallel analysis of the samples, and wherein the analyzing comprises:
(i) setting a first bias model using the genetic data for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest from the at least one diploid sample determined to be disomic for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest,
(ii) normalizing the genetic data for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest for the test sample using the first bias model, and
(iii) determining the likelihood of aneuploidy for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest in the test sample using the normalized data, wherein the normalized data comprise quantitative allelic data from a plurality of polymorphic loci in the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest and quantitative non-allelic data from a plurality of polymorphic and/or non-polymorphic loci in the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest, and wherein the determining the likelihood of aneuploidy comprises obtaining a first probability value indicating the likely copy number of the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest by quantitative allelic analysis of the allelic data, obtaining a second probability value indicating the likely copy number of the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest by quantitative non-allelic analysis of the non-allelic data, and combining the first probability value and the second probability value to produce a combined probability value to determine the likely copy number of the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest,
wherein the quantitative allelic analysis is performed by quantitative allelic maximum likelihood method or het rate method, and wherein the quantitative non-allelic analysis is performed by quantitative non-allelic maximum likelihood method or QMM method and the het rate method is based on analysis of observed allele ratios at each SNP using a joint distribution model, and wherein the QMM method is based on analysis of the number of sequencing reads at each SNP,
wherein the at least one diploid sample is determined to be disomic for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest by analyzing the genetic data from the parallel analysis, and
wherein the likelihood of aneuploidy is determined by:
creating a plurality of ploidy hypotheses wherein each ploidy hypothesis is associated with a specific copy number for the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest,
determining a ploidy probability value for each ploidy hypothesis, wherein the ploidy probability value indicates the likelihood that the target sample has the number of copies of the chromosome or chromosome segment of interest that is associated with the ploidy hypothesis, wherein the ploidy probability values are derived from the normalized genetic data,
selecting the ploidy hypothesis with the maximum likelihood as the ploidy hypothesis most likely to be correct; and
outputting the likely ploidy state of the test sample as an indication of the likelihood of aneuploidy.
|