| CPC G01V 1/306 (2013.01) [E21B 44/005 (2013.01); G01V 1/284 (2013.01); G01V 2210/626 (2013.01); G01V 2210/646 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
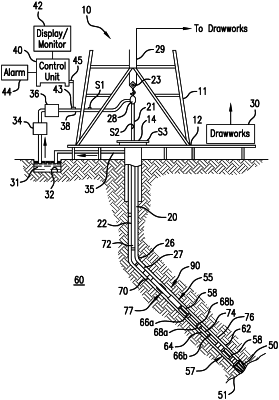
1. A downhole measurement system comprising:
a bottomhole assembly configured to drill a borehole through a formation, the bottomhole assembly comprising a circumference and a longitudinal axis, the bottomhole assembly configured to rotate in the formation around the longitudinal axis by an azimuthal angle;
a sensor assembly configured to provide four component cross multipole measurements, the sensor assembly comprising:
at least one multipole transmitter configured to transmit acoustic signals at a first azimuthal angle and a second azimuthal angle of the rotation of the bottomhole assembly into the formation, the at least one multipole transmitter located in, on, or at the bottomhole assembly, wherein the at least one multipole transmitter is of order n≥1; and
a first multipole receiver and a second multipole receiver, located on or at the bottomhole assembly, wherein the first multipole receiver is circumferentially aligned with the at least one multipole transmitter and the second multipole receiver is circumferentially offset from the first multipole receiver, wherein the first and second multipole receivers are axially offset from the at least one multipole transmitter along the longitudinal axis of the bottomhole assembly, wherein the first multipole receiver and the second multipole receiver are of order n≥1; and
a controller configured to obtain first acoustic multipole data and second acoustic multipole data from the first multipole receiver, and third acoustic multipole data and fourth acoustic multipole data from the second multipole receiver, wherein the first and third acoustic multipole data are based on acoustic signals transmitted at the first azimuthal angle and the second and fourth acoustic multipole data are based on acoustic signals transmitted at the second azimuthal angle,
wherein the controller is configured to determine acoustic azimuthal anisotropy of the formation using the first, second, third, and fourth acoustic multipole data, a fast principal wave and a slow principal wave, wherein the fast principal wave and the slow principal wave are determined by using:
Ĝn(r,z,s)=RT(nθF)Q−1(nΔθ)P′(r,z,s)R(nθF)
wherein n is the order of the at least one multipole transmitter, Ĝn is a principal wave matrix, R is a rotation matrix, Q is an offset matrix, θ is an azimuthal angle, θF is an azimuthal angle of the fast polarization direction, P′ is an acoustic pressure data matrix, r is a radial position in the borehole, z is an axial location in the borehole, and s is a complex frequency.
|