| CPC G01S 13/9027 (2019.05) [G01S 13/9052 (2019.05); G01S 13/9054 (2019.05); G01S 13/9088 (2019.05)] | 20 Claims |
|
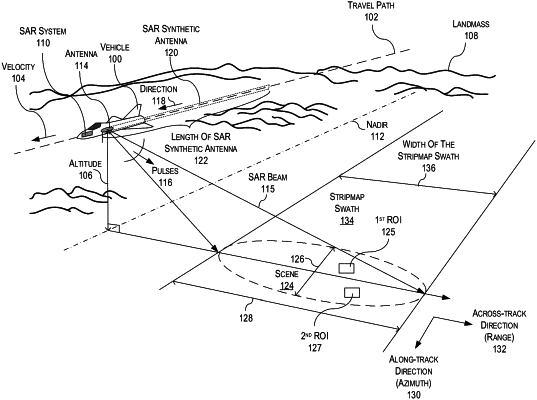
1. A method that extracts a region of interest (ROI) from composite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) phase history data, the method comprising:
receiving, by a SAR system, the composite SAR phase history data of a plurality of backscattered return signals produced as a result of the SAR system illuminating a scene with a SAR beam;
obtaining a location of a ROI within the scene; and
extracting from the composite SAR phase history data a component SAR phase history data corresponding to the ROI, wherein the component SAR phase history data is to be utilized for object detection;
wherein the extracting the composite SAR phase history data comprises: sectorizing the SAR beam into a plurality of sectors, wherein each sector is defined
between a first sectoral angle and a second sectoral angle and each sector corresponds to a Doppler frequency interval having a first frequency value and a second frequency value; and
decomposing the composite SAR phase history data into a plurality of sectoral SAR phase history data via Doppler processing of an induced azimuth signal,
wherein each sectoral SAR phase history data corresponds to a unique sector of the plurality of sectors, the component SAR phase history data corresponds to a first sectoral SAR phase history data corresponding to a first sector of the plurality of the sectors, and the first sector corresponds to a first Doppler frequency interval;
wherein the Doppler processing of the induced azimuth signal includes:
determining a first Doppler frequency in the induced azimuth signal from the backscattered return signals received at a first directional angle (θ1) from the normal direction to the travel path, wherein the first Doppler frequency (f1) is defined by the first directional angle, a velocity of the SAR system along the travel path and a wavelength of a carrier frequency of the SAR system, and
bandpass filtering the induced azimuth signal, with a bandpass filter having a passband, to produce a new induced azimuth signal that includes frequency components of the induced azimuth signal that fall within the passband.
|