| CPC C12Q 1/6841 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6806 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6816 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6823 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6876 (2013.01)] | 28 Claims |
|
1. A method for sample analysis, comprising:
a) providing a biological sample immobilized on a substrate, wherein the biological sample is fixed;
b) contacting the biological sample with a catalyst that catalyzes de-crosslinking of molecular crosslinks in the biological sample, wherein the catalyst is a compound of formula (I),
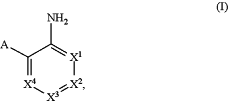 or a salt, zwitterion, or solvate thereof, wherein:
A is selected from the group consisting of —COOH, —P(═O)(OH)2, and S(═O)2OH;
X1, X2, X3, and X4 are each independently selected from the group consisting of: CH, CRa, and N;
each occurrence of Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 haloalkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, —NO2, —NR′R″, and —C(═O)NR′R″; and
each occurrence of R′ and R″ is independently selected from the group consisting of H and C1-6 alkyl which is optionally substituted with
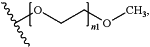 wherein n1 is an integer from 12 to 16;
c) contacting the biological sample with a nucleic acid probe that directly or indirectly binds to an RNA analyte at a location in the biological sample;
d) circularizing the nucleic acid probe to form a circularized nucleic acid probe;
e) using a polymerase to perform rolling circle amplification (RCA) using the circularized nucleic acid probe as template to generate an RCA product, optionally wherein the polymerase is a phi29 polymerase; and
f) detecting an optical signal associated with the RCA product, thereby detecting the RNA analyte at the location in the biological sample.
|