| CPC C07D 498/04 (2013.01) [A61P 35/00 (2018.01); C07D 471/04 (2013.01); C07D 487/04 (2013.01); C07D 491/107 (2013.01); C07D 513/04 (2013.01); C07D 519/00 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A compound of formula (I′):
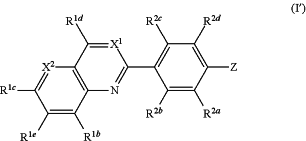 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or hydrate thereof, wherein:
X1 is C(R1a) and X2 is N;
Z is selected from the group consisting of:
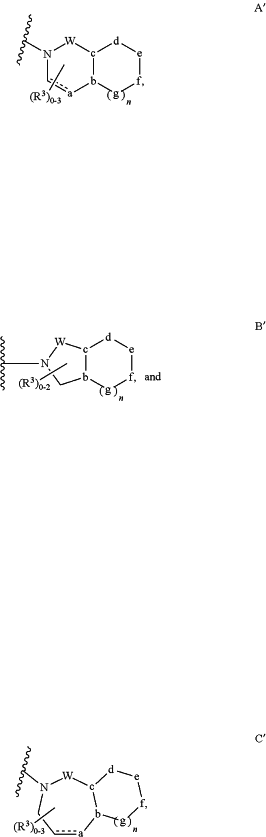 wherein:
the dashed bonds are single or double bonds,
n is 0 or 1, and
W is —C(O)— or —SO2—;
each of ring vertices a, b, c, d, e, f, and g are independently selected from the group consisting of O, S, N, C(R4), and N(R4), and the bonds joining the ring vertices are independently single or double bonds;
each R1a, R1b, R1c, R1d and R1e is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, deuterium, halogen, —CN, —NO2, —Rc, —CO2Ra, —CONRaRb, —C(O)Ra, —OC(O)NRaRb, —NRbC(O)Ra, —NRbC(O)2Rc, —NRaC(O)NRaRb, —NRaRb, —ORa, and —S(O)2NRaRb, wherein each Ra and Rb is independently selected from hydrogen, C1-8 alkyl, C3-6 cycloalkyl, and C1-8 haloalkyl, or Ra and Rb, when attached to the same nitrogen atom, can be combined with the nitrogen atom to form a four-, five-, or six-membered ring having from 0 to 2 additional heteroatoms as ring members selected from N, O, S, SO, and SO2; each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of C1-8 alkyl, C1-8 haloalkyl, C1-8 deuteroalkyl, C2-6 alkenyl, C2-6 alkynyl, and C3-6 cycloalkyl, and wherein the aliphatic and cyclic portions of Ra, Rb and Rc can be further substituted with from one to three halogen, hydroxy, C1-4 alkyl, C1-4 alkoxy, amino, C1-4 alkylamino, di C1-4 alkylamino, or carboxylic acid groups;
each R2a, R2b, R2c and R2d is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, C1-3 alkyl, C1-3 deuteroalkyl, C1-3 haloalkyl, C1-3 alkoxy, C1-3 deuteroalkoxy, and C1-3 haloalkoxy;
R3 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, deuterium, C1-3 alkyl, C1-3 deuteroalkyl, C1-3 alkylene-ORd, C1-3 alkylene-CO2Rd, C1-3 alkylene-NRdRe, C1-3 alkylene-CONRdRe, C1-3 alkylene-OC(O)NRdRe, and C1-3 alkylene-NReC(O)2Rf;
each R4 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, —CN, —Rf, —CO2Rd, —CONRdRe, —C(O)Rd, —OC(O)NRdRe, —NReC(O)Rd, —NReC(O)2Rf, —NReC(O)NRdRe, —NRdRe, —ORd, —S(O)2NRdRe, —Xa—CN, —Xa—CO2Rd, —Xa—CONRdRe, —Xa—C(O) Rd, —Xa—OC(O)NRdRe, —Xa—NReC(O)Rd, —Xa—NReC(O)2Rf, —Xa—NRdC(O)NRdRe, —Xa—NRdRe, —Xa—ORd, —Xa—S(O)2NRdRe, and —Xa—OP(O)(OH)2, wherein each Xa is independently C1-6 alkylene;
each Rd and Re is independently selected from hydrogen, C1-8 alkyl, and C1-8 haloalkyl, or Rd and Re, when attached to the same nitrogen atom, can be combined with the nitrogen atom to form either (i) a four-, five-, or six-membered ring having from 0 to 3 additional heteroatoms as ring members selected from N, O, C(O), S, SO, and SO2, or (ii) a spiroheterocycloalkyl ring;
each Rf is independently selected from the group consisting of C1-8 alkyl, C1-8 haloalkyl, C1-8 deuteroalkyl, C3-6 cycloalkyl, C3-6 heterocycloalkyl, phenyl, and 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl; and
the aliphatic and cyclic portions of Rd, Re and Rf can be further substituted with from one to three halogen, hydroxy, benzyloxy, C1-4 alkyl, C1-4 alkoxy, amino, C1-4 alkylamino, di C1-4 alkylamino, tetrazolyl, or carboxylic acid groups.
|