| CPC A61B 18/02 (2013.01) [F25B 19/005 (2013.01); A61B 2018/0262 (2013.01); A61B 2018/0293 (2013.01); A61B 2090/378 (2016.02)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A device for percutaneous cryotherapy comprising:
a probe comprising an outer surface defining an inner lumen and wherein the probe is configured to be inserted percutaneously;
a backend component configured to be coupled to the probe, wherein the backend component is configured to be connected to a source of carbon dioxide gas;
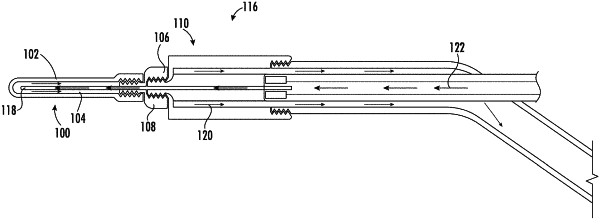
a Joule-Thomson nozzle disposed within the backend component; and
a flow path configured to direct incoming gas of the carbon dioxide gas to flow through the Joule-Thomson nozzle, out of the Joule-Thomson nozzle, into the inner lumen of the probe, and back out through the backend component via a first area within a first lumen in the backend component and outside of the Joule-Thomson nozzle,
wherein the Joule-Thomson nozzle extends into a second lumen in the backend component and the second lumen is configured to carry the incoming gas from the source of carbon dioxide gas to the Joule-Thomson nozzle,
wherein a first portion of the second lumen extends into the backend component and a second portion of the second lumen extends outside the backend component, and
wherein the second lumen is wider than the Joule-Thomson nozzle,
wherein a first portion of the Joule-Thomson nozzle that extends into the second lumen is surrounded by another material between the first portion of the Joule-Thomson nozzle and the second lumen,
wherein a second portion of the Joule-Thomson nozzle that extends into the second lumen further extends into the second lumen beyond the other material and ends within the second lumen, and
wherein the backend component is further configured to include a choke point portion configured to throttle the incoming gas, flowing from the second lumen and into the Joule-Thomson nozzle, to decrease a temperature of the incoming gas,
wherein the choke point portion is comprised of at least the first portion of the Joule-Thomson nozzle, the second portion of the Joule-Thomson nozzle, the other material, and the first portion of the second lumen, and
wherein the choke point portion throttles the incoming gas via a difference between a first width of the second lumen and a second width of the Joule-Thomson nozzle.
|