| CPC G06T 5/005 (2013.01) [G06F 18/2113 (2023.01); G06T 7/194 (2017.01); G06T 7/269 (2017.01); G06T 7/70 (2017.01); G06V 10/751 (2022.01); G06V 20/49 (2022.01); G11B 27/036 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06V 30/10 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
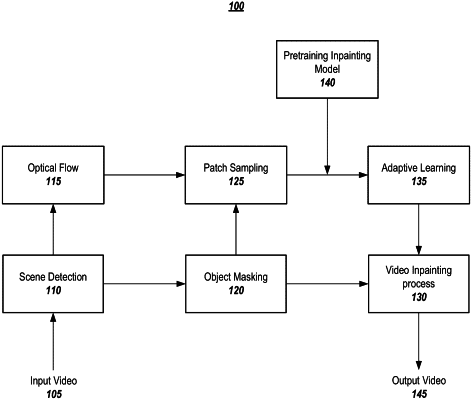
splitting an input video into a set of video sequences, which comprise one or more video frames;
generating one or more object masks, which represent one or more areas comprising an object or objects targeted to be removed and inpainted in the video sequences;
generating optical flows for each video sequence; and
for each video sequence from the set of video sequences:
adaptively training an inpainting model, which has been pretrained, using, as inputs into the inpainting model independent from being input, if at all, into a loss function, masked patch samples, in which patch samples were selected from the video sequence using at least some of the optical flows to obtain an updated inpainting model; and
using the updated inpainting model to modify the video sequence to inpaint at least part of the video sequence.
|