| CPC C12P 5/026 (2013.01) [C12N 9/1205 (2013.01); C12N 9/1229 (2013.01); C12N 9/1235 (2013.01); C12N 9/88 (2013.01); C12N 15/52 (2013.01); C12P 5/002 (2013.01); C12Y 402/03 (2013.01); Y02E 50/30 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A method for producing an alkene comprising culturing a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having an alkene pathway under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce said alkene, wherein said non-naturally occurring microbial organism comprises at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a alkene pathway enzyme expressed in sufficient amount to convert an alcohol to said alkene, wherein said alkene pathway comprises alkene pathway enzymes selected from:
(1) an alcohol kinase that transfers a phosphate group to a hydroxyl group, and a phosphate lyase that converts an alkyl-phosphate to an alkene, wherein the alcohol kinase is selected from enzymes having an E.C. number selected from the group consisting of 2.7.1.30 (glycerol kinase), 2.7.1.36 (mevalonate kinase), or 2.7.1.39 (homoserine kinase);
(2) a diphosphokinase that transfers a di-phosphate group to a hydroxyl group and a diphosphate lyase that converts an alkyl di-phosphate to an alkene, wherein the diphosphokinase is selected from enzymes having an E.C. number selected from the group consisting of, 2.7.6.1 (ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase) or 2.7.6.2 (thiamine diphosphokinase); and
(3) an alcohol kinase that transfers a phosphate group to a hydroxyl group, an alkyl phosphate kinase that transfers a phosphate group to a phosphate group of an alkyl-phosphate, and a diphosphate lyase that converts an alkyl di-phosphate to an alkene, wherein:
(i) the alcohol kinase is selected from enzymes having an E.C. number selected from the group consisting of 2.7.1.30 (glycerol kinase), 2.7.1.36 (mevalonate kinase), or 2.7.1.39 (homoserine kinase);
(ii) the alkyl phosphate kinase is selected from enzymes having an E.C. number selected from the group consisting of 2.7.4.2 (phosphomevalonate kinase), 2.7.4.18 (farnesyl-diphosphate kinase); and
(iii) the diphosphate lyase is selected from enzymes having an E.C. number selected from the group consisting of 4.2.3.5 (Chorismate synthase), 4.2.3.15 (Myrcene synthase), 4.2.3.36 (Terpentriene synthase), 4.2.3.46 ((E, E)-alpha-Farnesene synthase), or 4.2.3.47 (Beta-Farnesene synthase);
wherein said alcohol is a compound of Formula (I)
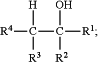 wherein said alkene is a compound of Formula (II)
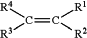 wherein,
(a) R1, R2, R3, and R4 of Formula I and R1, R2, R3, and R4 of Formula II are the same and are independently hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, or ethenyl, and
(b) wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are selected such that the compound of Formula (II) is a C4 alkene.
|