| CPC B41J 2/0458 (2013.01) [B41J 2/04585 (2013.01); B41J 2002/14475 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
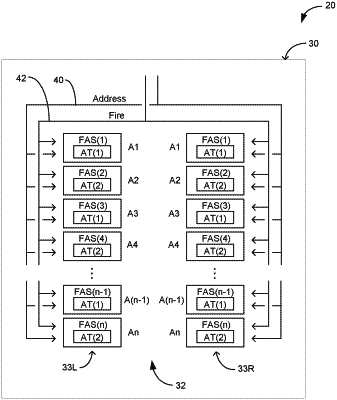
1. A fluidic circuit comprising:
a plurality of fluidic actuation structures on a substrate, the plurality of fluidic actuation structures comprising:
a first set of fluidic actuation structures; and
a second set of fluidic actuation structures, the first set of fluidic actuation structures and the second set of fluidic actuation structures having respective column positions;
wherein each fluidic actuation structure in the first set of fluidic actuation structures and in the second set of fluidic actuation structures is addressable by an actuation address from a set of actuation addresses;
wherein the each fluidic actuation structure in the first set of fluidic actuation structures has a same actuation address as another fluidic actuation structure in the second set of fluidic actuation structures;
wherein a location along a column of the another fluidic actuation structure in the second set of fluidic actuation structures that has the same actuation address as the each fluidic actuation structure in the first set of fluidic actuation structures is offset relative to the location of the each fluidic actuation structure in the first set of fluidic actuation structures; and
wherein an address encoder is configured to drive the set of actuation addresses onto an address bus associated with the plurality of fluidic actuation structures.
|