| CPC A61N 1/3688 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02444 (2013.01); A61B 5/026 (2013.01); A61B 5/1107 (2013.01); A61B 5/287 (2021.01); A61B 5/349 (2021.01); A61B 5/352 (2021.01); A61B 5/686 (2013.01); A61N 1/025 (2013.01); A61N 1/0573 (2013.01); A61N 1/36507 (2013.01); A61N 1/36578 (2013.01); A61N 1/36585 (2013.01); A61N 1/36592 (2013.01); A61N 1/3704 (2013.01); A61N 1/37211 (2013.01); A61N 1/3756 (2013.01); A61B 5/1118 (2013.01); A61N 1/36542 (2013.01); A61N 1/3682 (2013.01); A61N 1/37205 (2013.01); A61N 1/37288 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A medical device, comprising:
a pulse generator configured to deliver cardiac pacing pulses;
a motion sensor configured to produce a motion signal;
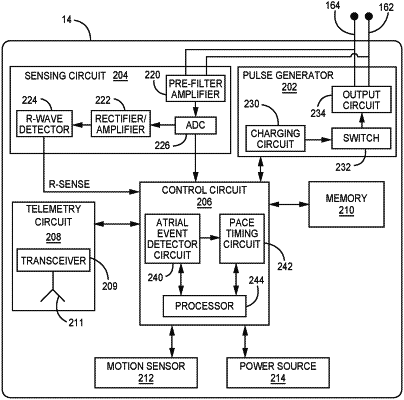
a sensing circuit configured to receive a cardiac electrical signal and sense R-waves from the cardiac electrical signal;
a control circuit coupled to the motion sensor, the sensing circuit, and the pulse generator, the control circuit configured to:
identify a ventricular systolic event as one of a ventricular pacing pulse delivered by the pulse generator or an R-wave sensed by the sensing circuit;
detect a ventricular passive filling event signal from the motion signal;
determine a time interval from the ventricular systolic event to the ventricular passive filling event; and
establish a minimum rate response pacing interval based on the time interval from the ventricular systolic event to the ventricular passive filling event, the minimum rate response pacing interval corresponding to a maximum pacing rate; and
a memory in communication with the control circuit and configured to store the minimum rate response pacing interval; and
the pulse generator is configured to deliver one or more pacing pulses at the maximum pacing rate.
|