| CPC H04B 10/70 (2013.01) [G06N 10/00 (2019.01); H04B 10/548 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
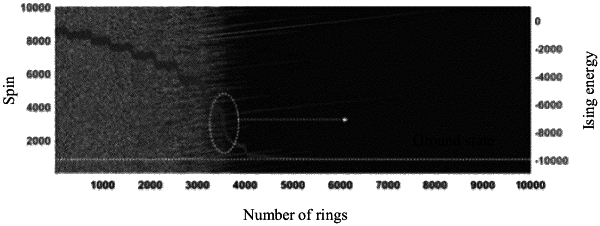
1. A microwave photonic Ising machine, comprising:
a closed loop comprising a phase and electro-optical conversion module and a storage, correlation and photoelectric conversion module connected in turn;
a laser light source configured to generate an optical signal and input the optical signal to the phase and electro-optical conversion module; and
a microwave pulse local oscillator source configured to generate a microwave pulse signal and input the microwave pulse signal to the phase and electro-optical conversion module;
wherein the phase and electro-optical conversion module is configured to modulate the microwave pulse signal, the optical signal, and a phase-specific two-phase microwave pulse spin electrical signal input by the storage, correlation and photoelectric conversion module, so as to obtain a phase-specific two-phase microwave pulse spin optical signal, and input the phase-specific two-phase microwave pulse spin optical signal to the storage, correlation and photoelectric conversion module for further storage and correlation; and
wherein the phase-specific two-phase microwave pulse spin electrical signal corresponds to a minimum gain state of the microwave photonic Ising machine.
|