| CPC G06F 12/0253 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0604 (2013.01); G06F 3/0631 (2013.01); G06F 3/0679 (2013.01); G06F 2212/7205 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system garbage collection method, comprising:
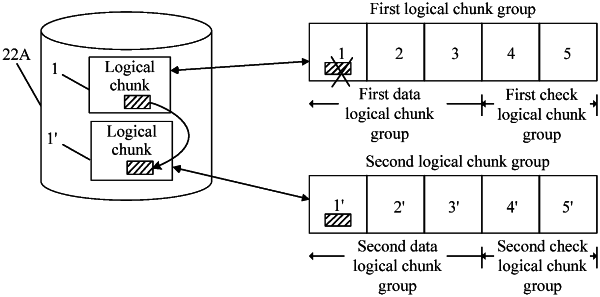
determining a first logical chunk group comprising a plurality of first data logical chunks, wherein the first data logical chunks are in a plurality of solid-state disks (SSDs) of a flash memory array, wherein at least one of the first data logical chunks comprises valid data, wherein a location of the valid data is a first logical address of the first data logical chunks, wherein there is a first correspondence between the first logical address and an actual address of a first solid-state disk of the solid-state disks in which the valid data is stored, wherein the first logical chunk group further comprises a first check logical chunk distributed in a second solid-state disk that is different from the solid-state disks, and wherein the second logical chunk group further comprises a second check logical chunk distributed in a third solid-state disk that is different from the solid-state disks;
creating a second logical chunk group comprising a plurality of second data logical chunks, wherein at least one of the second data logical chunks is distributed in the first solid-state disk;
allocating a second logical address in at least one of the second data logical chunks to the valid data; and
instructing the first solid-state disk to modify the first correspondence to a second correspondence between the second logical address and the actual address.
|