| CPC G01S 19/215 (2013.01) [G01S 19/03 (2013.01); G01S 19/36 (2013.01); G01S 19/24 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
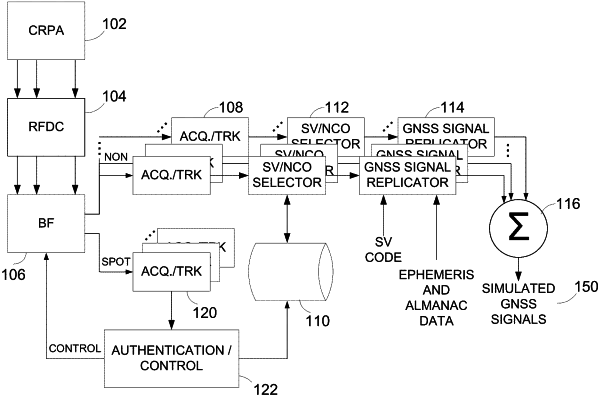
1. An apparatus comprising a first global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver configured to provide anti-spoofing capability to a second GNSS receiver, the apparatus comprising:
an acquisition and tracking circuit comprising at least a matched filter, the acquisition and tracking circuit configured to track a plurality downconverted signals;
a processor configured to determine which of the plurality of downconverted signals are based on authentic GNSS signals and which of the plurality of downconverted signals are based on spoofed GNSS signals;
a beamformer at least partially controlled by the processor, wherein the beamformer has at least a first output with a first group of signals and a second output with a second group of signals, wherein the first output corresponds to a first antenna pattern and the second output corresponds to a second antenna pattern different than the first antenna pattern, wherein the first group of signals is provided as an input to the acquisition and tracking circuit; and
wherein the processor is configured to determine whether a particular downconverted signal is based on an authentic GNSS signal or on a spoofed GNSS signal.
|