| CPC H10K 85/761 (2023.02) [A23B 7/015 (2013.01); A23B 7/154 (2013.01); A61L 2/0052 (2013.01); A61L 2/0076 (2013.01); A61L 2/084 (2013.01); A61L 2/088 (2013.01); A61N 5/062 (2013.01); A61N 5/0624 (2013.01); B01D 29/62 (2013.01); B01D 46/66 (2022.01); C07K 14/43504 (2013.01); C07K 14/43586 (2013.01); C07K 19/00 (2013.01); C09K 11/06 (2013.01); H01G 9/2018 (2013.01); H10K 30/30 (2023.02); H10K 30/82 (2023.02); A23V 2002/00 (2013.01); A61N 2005/0663 (2013.01); C07K 2319/00 (2013.01); C09K 2211/14 (2013.01); H01G 9/2059 (2013.01); H10K 2102/00 (2023.02); H10K 2102/102 (2023.02); H10K 2102/103 (2023.02); Y02E 10/549 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
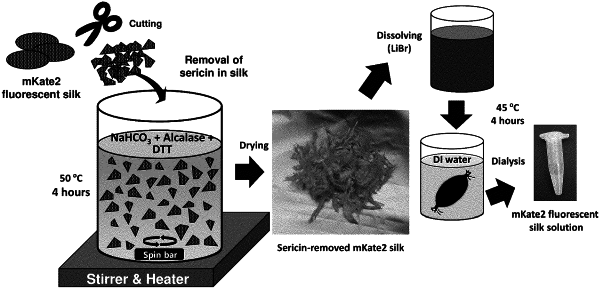
|
1. A method of disinfection of a surface of an object exposed to or attached to harmful microorganisms including pathogenic bacteria and viruses, comprising:
placing a predetermined quantity of a hybridized fluorescent silk i) directly on to a skin surface of a subject; or ii) on a medium and then placing the medium on the skin surface of the subject;
applying light in the visible spectrum for a predetermined amount of time to the placed quantity of the hybridized fluorescent silk, wherein the hybridization is based on red fluorescent protein.
|