| CPC H04L 9/3221 (2013.01) [H04L 9/0618 (2013.01); H04L 9/0643 (2013.01); H04L 9/0894 (2013.01); H04L 9/50 (2022.05)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
a sending system comprising a processor configured to:
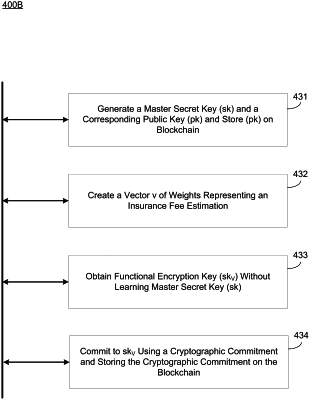
receive, via an oblivious transfer protocol between the sending system and a receiving system, a data vector of the receiving system, wherein the sending system does not learn the data vector the vector comprises: sensitive fee values that are used by the receiving system;
generate a master key of the sending system;
generate, using a key derivation function implemented by the sending system, a plurality of derived functional encryption keys corresponding to all possible combinations of data elements of the data vector based on the master key;
send, via the oblivious transfer protocol, a correct functional encryption key, of the plurality of derived functional encryption keys, to the receiving system, the correct functional encryption key corresponding to the data vector, wherein the sending system does not learn which of the plurality of derived functional encryption keys is the correct functional encryption key;
sign a zero-knowledge proof (ZKP), generated by the receiving system, of the correct functional encryption key to commit the sending system to the correct functional encryption key; and
store the commitment to the functional encryption key in a blockchain.
|