| CPC H04L 63/164 (2013.01) [G06F 16/93 (2019.01); G06F 21/33 (2013.01); G06F 21/604 (2013.01); G06F 21/6218 (2013.01); H04L 43/55 (2022.05); H04L 63/102 (2013.01); G06F 3/0601 (2013.01); G06F 21/125 (2013.01); G06F 21/31 (2013.01); G06F 21/316 (2013.01); G06F 21/52 (2013.01); G06F 21/577 (2013.01); H04L 63/08 (2013.01); H04L 63/1441 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
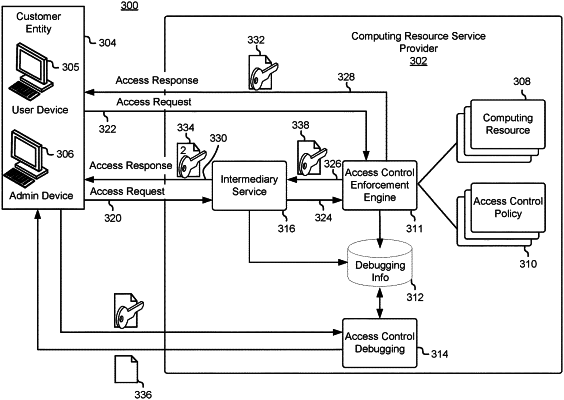
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising: sending, by an intermediary service to an access enforcement engine, an access request including a first indication that identifies the access request as a simulation mode request, the sending of the access request being initiated based at least in part on receiving a second request from a customer of a computing resource service provider, the simulation mode request being an access request which is not to be serviced, and wherein the access enforcement engine is capable of granting the access request;
receiving a second indication, without the access request being serviced, that indicates whether the access request would be authorized had the access request not been the simulation mode request, the second indication being associated with a token, the token being responsive to the access request and encoding information usable for obtaining detailed information regarding an evaluation of one or more access control policies associated with the customer;
augmenting the token to produce an augmented token, the token being augmented to include context information associated with the second request obtained from the customer;
encrypting the augmented token for decrypting by the customer;
sending the augmented token to the customer; and
obtaining from the customer a remediation guidance request associated with the access request, the remediation guidance request including the augmented token.
|