| CPC H02M 1/0003 (2021.05) [H02M 1/083 (2013.01); H02M 1/4233 (2013.01); H02M 7/1626 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
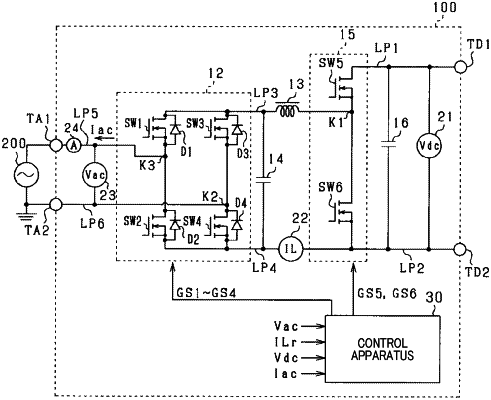
1. A control apparatus for a power conversion apparatus that includes a reactor, a first alternating-current-side terminal, a second alternating-current-side terminal, a first direct-current-side terminal, a second direct-current-side terminal, and a full-bridge circuit that is provided between the alternating-current-side terminals and the reactor,
the power conversion apparatus being provided with at least either of a function for converting an alternating-current voltage of an alternating-current power supply that is inputted from the alternating-current-side terminals to a direct-current voltage and outputting the direct-current voltage from the direct-current-side terminals, and a function for converting a direct-current voltage that is inputted from the direct-current-side terminals to an alternating-current voltage and outputting the alternating-current voltage from the alternating-current-side terminals, wherein
the full-bridge circuit has a series-connection body of a first switch and a second switch, and a series-connection body of a third switch and a fourth switch, and is configured by the series-connection bodies being connected in parallel;
diodes are respectively connected in antiparallel to the first switch, the second switch, the third switch, and the fourth switch,
a connection point between the first switch and the second switch is connected to the first alternating-current-side terminal,
a connection point between the third switch and the fourth switch is connected to the second alternating-current-side terminal,
the control apparatus includes:
a detected voltage acquiring unit that acquires a detected voltage that is a voltage value of the alternating-current power supply that is detected by a voltage sensor;
a polarity determining unit that determines a period from when the detected voltage exceeds a first determination value for determining a zero-up-crossing timing of an actual voltage that is an actual voltage value of the alternating-current power supply until the detected voltage falls below a second determination value for determining a zero-down-crossing timing of the actual voltage to be a period during which the actual voltage has a positive polarity, and determines a period from when the detected voltage falls below the second determination value until the detected voltage exceeds the first determination value to be a period during which the actual voltage has a negative polarity, wherein the first determination value is a voltage value that is less than the detected voltage when the actual voltage is zero, and the second determination value is a voltage value that is greater than the detected voltage when the actual voltage is zero; and
an operating unit that alternately switches a set that is set to an ON state, of a set of the first switch and the fourth switch and a set of the second switch and the third switch, each time the polarity of the actual voltage that is determined by the polarity determining voltage is switched.
|