| CPC G10L 21/0232 (2013.01) [G10L 25/18 (2013.01); G10L 25/30 (2013.01); H04R 1/406 (2013.01); H04R 3/005 (2013.01); G10L 2021/02082 (2013.01); G10L 2021/02166 (2013.01); H04R 2201/401 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
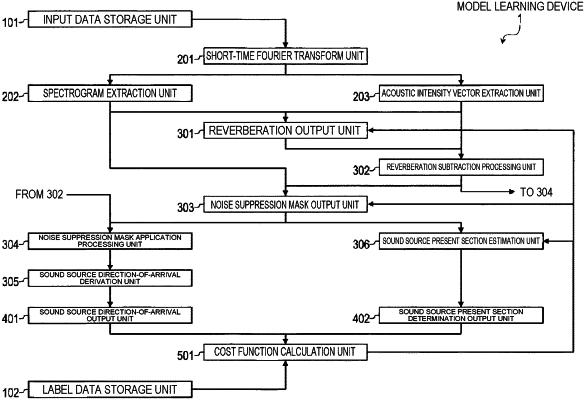
1. A direction-of-arrival estimation device comprising a processor configured to execute a method comprising:
receiving input of a real spectrogram extracted from a complex spectrogram of acoustic data and an acoustic intensity vector extracted from the complex spectrogram;
generating an estimated reverberation portion of the acoustic intensity vector;
receiving input of the real spectrogram and the acoustic intensity vector from which the reverberation portion has been subtracted;
generating a time frequency mask for noise suppression; and
determining a sound source direction-of-arrival based on an acoustic intensity vector formed by applying the time frequency mask to the acoustic intensity vector from which the reverberation portion has been subtracted.
|