| CPC G10L 15/20 (2013.01) [G06F 17/18 (2013.01); G10L 15/16 (2013.01); G10L 25/24 (2013.01); G10L 25/78 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
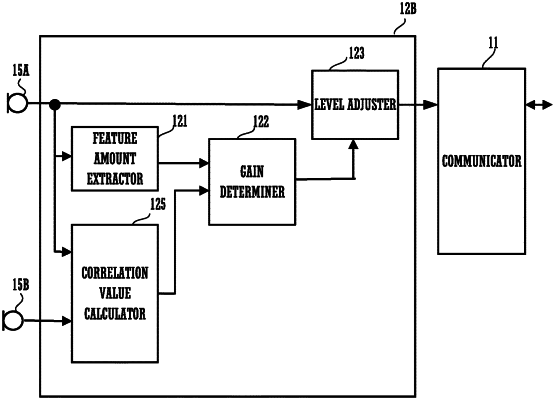
1. A voice processing method comprising:
collecting a first audio signal collected by a first microphone from a sound source and a second audio signal collected by a second microphone from the sound source;
estimating probability of the first audio signal including a person's voice;
setting a probability value to:
a first probability value indicative of the first audio signal including a person's voice; and
a second probability value of zero indicative of the first audio signal not including a person's voice;
estimating a correlation value of the first audio signal and the second audio signal;
obtaining a time difference between waveforms of the first audio signal and the second audio signal based on the estimated correlation value;
determining that the first audio signal:
includes a person's voice, in a state where the time difference is greater than a predetermined value; and
does not include a person's voice, in a state where the time difference is not greater than the predetermined value;
determining a gain of the first audio signal to be:
from among a range of greater than zero and less than one, in a state where the first probability value is set and the time difference is greater than the predetermined value; and
zero, in a state where the time difference is not greater than the predetermined value;
processing the first audio signal based on the determined gain of the first audio signal to improve an audio quality at a far-end side; and
sending the processed audio signal to the far-end side, where a voice processing device located at the far-end side reproduces the received processed audio signal to emit sound from a speaker.
|